Calculate exponential of a value in Julia – exp(), exp10(), exp2(), expm1() and frexp() Methods
Last Updated :
26 Mar, 2020
The
exp() is an inbuilt function in
julia which is used to calculate the natural base exponential of the specified number.
Syntax: exp(x)
Parameters:
Returns: It returns the calculated natural base exponential of the specified number.
Example:
println(exp(0))
println(exp(1))
println(exp(5))
println(exp(-1))
|
Output:
1.0
2.718281828459045
148.4131591025766
0.36787944117144233
exp10()
The
exp10() is an inbuilt function in
julia which is used to calculate the base 10 exponential of the specified number.
Syntax: exp10(x)
Parameters:
Returns: It returns the calculated base 10 exponential of the specified number.
Example:
println(exp10(0))
println(exp10(1))
println(exp10(10))
println(exp10(-1))
|
Output:
1.0
10.0
1.0e10
0.1
exp2()
The
exp2() is an inbuilt function in
julia which is used to calculate the base 2 exponential of the specified number.
Syntax: exp2(x)
Parameters:
Returns: It returns the calculated base 2 exponential of the specified number.
Example:
println(exp2(0))
println(exp2(1))
println(exp2(2))
println(exp2(-1))
|
Output:
1.0
2.0
4.0
0.5
expm1()
The
expm1() is an inbuilt function in
julia which is used to accurately calculate
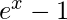
.
Syntax: expm1(x)
Parameters:
Returns: It returns the calculated value of 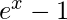 .
.
Example:
println(expm1(0))
println(expm1(1))
println(expm1(2))
println(expm1(-1))
|
Output:
0.0
1.718281828459045
6.38905609893065
-0.6321205588285577
frexp()
The
frexp() is an inbuilt function in
julia which is used to return (x, exp), where x is given and having a magnitude in the interval [1/2, 1) or 0.
Syntax: frexp(x)
Parameters:
- x: Specified values in the interval [1/2, 1) or 0.
Returns: It returns (x, exp), where x is given and having a magnitude in the interval [1/2, 1) or 0.
Example:
println(frexp(0.6))
println(frexp(0.5))
println(frexp(0.7))
println(frexp(0.9999))
|
Output:
(0.6, 0)
(0.5, 0)
(0.7, 0)
(0.9999, 0)
Please Login to comment...