Overview of Room in Android Architecture Components
Last Updated :
09 May, 2021
Room is one of the Jetpack Architecture Components in Android. This provides an abstract layer over the SQLite Database to save and perform the operations on persistent data locally. This is recommended by Google over SQLite Database although the SQLite APIs are more powerful they are fairly low-level, which requires a lot of time and effort to use. But Room makes everything easy and clear to create a Database and perform the operations on it.
Why use Room?
- Cache the relevant pieces of the data so that when the user’s device is offline, they can still browse and view the content offline.
- Compile-time SQLite query verification preserves the application from crashing.
- The annotations which it provides minimizes the boilerplate code.
- This also provides easy integration with the other Architecture Components like LiveData, LifecycleObserver, etc., You can take codelab provided by Google here.
Difference Between Room and SQLite
|
Room
|
SQLite
|
| No need of writing raw queries. |
Need to write raw queries. |
| Compile Time verification of SQL queries. |
No, compile-time boilerplate verification of SQL queries. |
| No need of converting the Data to Java Objects. As Room internally maps the Database objects to Java objects. |
Need to write SQL queries to convert the Data to Java Objects. |
| This conveniently supports the integration with other Architecture components. |
This needs a lot of boiler plate code to integrate with the other Architecture Components. |
| Room provides easier way to work with LiveData and perform the operations. |
SQLite doesn’t provide a direct way to access the LiveData, it needs external code to be written to access the LiveData. |
| There is no need to change the code when the database schema gets changes. |
This needs to change its queries whenever the database schema gets changes |
Primary Components of Room
- Database Class: This provides the main access point to the underlying connection for the application’s persisted data. And this is annotated with @Database.
- Data Entities: This Represents all the tables from the existing database. And annotated with @Entity.
- DAO (Data Access Objects): This contains methods to perform the operations on the database. And annotated with @Dao.
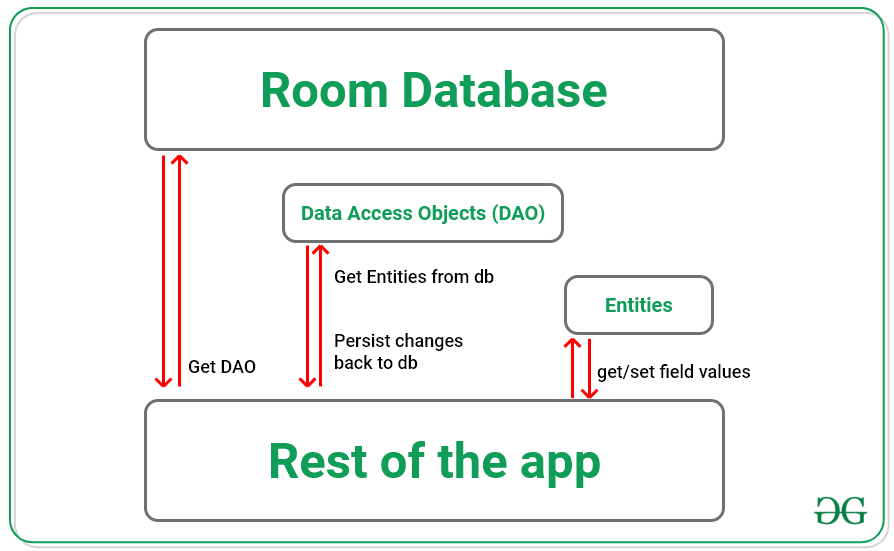
Room Library Architecture
From the image below we can conclude the working of the Room database as The application first gets the Data Access Objects (DAOs) associated with the existing Room Database. After getting DAOs, through DAOs it accesses the entities from the Database Tables. And then it can perform the operations on those entities and persist back the changes to the Database.
Steps to implement Room Database in Android Application
Step 1: Create an Empty Activity project
Step 2: Adding the required dependencies
- Add the following dependencies to the app-level gradle file. By going to ProjectName -> src -> build.gradle.
// room_version may vary
def room_version = “2.3.0”
implementation “androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version”
kapt “androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version”
implementation “androidx.room:room-ktx:$room_version”
testImplementation “androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version”
Now creating the components of Room one by one:
Note: Here the entities for every interface and classes created are important and to be taken care of.
Step 3: Creating Data Entity
- Create a sample Data class naming User.kt.
- And invoke the following code which contains entities User as an entity, which represents a row and first_name, last_name, age represents column names of the table.
Kotlin
import androidx.room.ColumnInfo
import androidx.room.Entity
import androidx.room.PrimaryKey
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true) val uid: Int,
@ColumnInfo(name = "name") val firstName: String?,
@ColumnInfo(name = "city") val lastName: String?
)
|
Step 4: Creating Data Access Objects (DAOs):
- Now create an interface named as UserDao.kt.
- And invoke the following code which provides various methods which are used by the application to interact with the user.
Kotlin
import androidx.room.Dao
import androidx.room.Delete
import androidx.room.Insert
import androidx.room.Query
@Dao
interface UserDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM user")
fun getAll(): List<User>
@Query("SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid IN (:userIds)")
fun loadAllByIds(userIds: IntArray): List<User>
@Insert
fun insertAll(vararg users: User)
@Delete
fun delete(user: User)
}
|
Step 5: Creating the Database
- Now creating the Database which defines the actual application’s database, which is the main access point to the application’s persisted data. This class must satisfy:
- The class must be abstract.
- The class should be annotated with @Database.
- Database class must define an abstract method with zero arguments and returns an instance of DAO.
- Now invoke the following code inside the AppDatabase.kt file.
Kotlin
import androidx.room.Database
import androidx.room.RoomDatabase
@Database(entities = arrayOf(User::class), version = 1)
abstract class UserDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun userDao(): UserDao
}
|
Step 6: Usage of the Room database
- Inside the MainActivity.kt file we can create a database, by providing custom names for the database.
Kotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.room.Room
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val DATABASE_NAME: String = "USER_DATABASE"
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val db = Room.databaseBuilder(
applicationContext, UserDatabase::class.java, DATABASE_NAME
).build()
val userDao = db.userDao()
val users: List<User> = userDao.getAll()
}
}
|
Note: By using this basic knowledge about Room Database one can build a basic CRUD application using Room Database by referring to How to Perform CRUD Operations in Room Database in Android?.
Please Login to comment...