PostgreSQL ILIKE query with SQLAlchemy
Last Updated :
02 Oct, 2023
The ILIKE is a pattern-matching approach provided by PostgreSQL. It is similar to the LIKE operator but it simply ignores the case. It is case-sensitive. For more understanding, you can visit this article on ILIKE operators. In this article, we will cover about PostgreSQL ILIKE query with SQLAlchemy.
PostgreSQL ILIKE Query
Step 1: Installation
We are using SQLAlchemy, psycopg2, pgAdmin, and Python. To install all these please refer to
Step 2: Creating Database and Table
We have created one database called SQLAlchemyPractice and a Table named Movies. We have inserted some dummy data using PgAdmin. We use a select command in SQL to display the resultset.
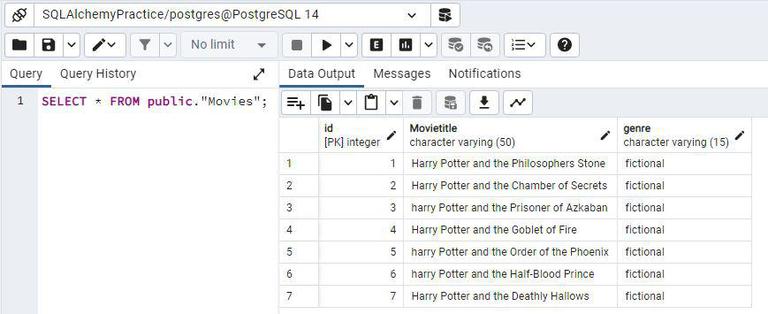
Data Present in Movies table
Step 3: Writing the Code
Importing Libraries: We are creating a simple program that fetches the data from the database using ilike_op() method in python. These are the libraries that we are going to use in our program. We sqlalchemy library that lubricates the transmission between python program and database.
import sqlalchemy as db
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy import URL
from sqlalchemy.sql.operators import ilike_op,like_op
Making Connection With Database: Here we are simply initializing our connection string. Psycopg2 is a postgresql database driver, it is used to perform operations on PostgreSQL using python. After that we provide username, password, host and database name. We pass connection string as a parameter in create_engine() to create an engine object. This will establish a connection with PostgreSQL.
url_object = URL.create(
"postgresql+psycopg2",
username="postgres",
password="gfg@123",
host="localhost",
database="SQLAlchemyPractice",
)
engine = create_engine(url_object)
Defining the Table Structure: Now we use db.MetaData() to define the structure of Table in terms of python data structure. After that we use db.Table() to define the data types of our attributes.
metadata_obj = db.MetaData()
db.Table(
'Movies',
metadata_obj,
db.Column('id', db.Integer, primary_key=True),
db.Column('Movietitle', db.String(50)),
db.Column('genre', db.String(15))
)
Syntax of like_op() and ilike_op()
- like_op(attribute, expression)
- ilike_op(attribute, expression)
attribute : Here we need to filter the data on the basis of Movie Title, So we use MOVIES.c.Movietitle.
expression : Here we need to provide the pattern of the data that we want to filter out. “%” is a wild card which represents zero, one or multiple characters. The pattern “h%” specifies that it will fetch all the Movietitle start with “h”.
Function for Filtering Movie Names Starting with ‘h’: Now we simply create MOVIES bucket and assign Movies matadata into it. We use filter() method, that filters the given sequence with the help of function that passed as a first argument. Here we pass ilike_op() as an argument. We use for loop in python to print our result set.
MOVIES = metadata_obj.tables['Movies']
query = db.select(MOVIES).filter(ilike_op(MOVIES.c.Movietitle, 'h%'))
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
Full Implementation for Filtering Using LIKE for Names of Movies with ‘h’
Python3
import sqlalchemy as db
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy import URL
from sqlalchemy.sql.operators import ilike_op,like_op
url_object = URL.create(
"postgresql+psycopg2",
username="postgres",
password="xyz@123",
host="localhost",
database="SQLAlchemyPractice",
)
engine = create_engine(url_object)
metadata_obj = db.MetaData()
db.Table(
'Movies',
metadata_obj,
db.Column('id', db.Integer, primary_key=True),
db.Column('Movietitle', db.String(50)),
db.Column('genre', db.String(15))
)
MOVIES = metadata_obj.tables['Movies']
query = db.select(MOVIES).filter(like_op(MOVIES.c.Movietitle, f'h%'))
result = engine.connect().execute(query).fetchall()
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
|
Output
It fetches all the movie titles start with ‘h’.
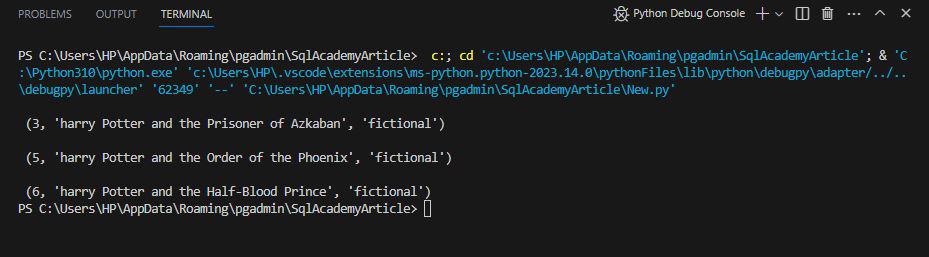
Output using like_op()
Implementation for Filtering Using ILIKE for Movie Names with ‘h’ and ‘H’
As you can see it only fetches Movietitle having a small case ‘h’ as it is case-sensitive. Now, we want to ignore the case of characters. We can use SQLAlchemy ilike_op() method on ‘Movietitle’. It has same syntax of like_op() method.
Python3
import sqlalchemy as db
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy import URL
from sqlalchemy.sql.operators import ilike_op,like_op
url_object = URL.create(
"postgresql+psycopg2",
username="postgres",
password="xyz@123",
host="localhost",
database="SQLAlchemyPractice",
)
engine = create_engine(url_object)
metadata_obj = db.MetaData()
db.Table(
'Movies',
metadata_obj,
db.Column('id', db.Integer, primary_key=True),
db.Column('Movietitle', db.String(50)),
db.Column('genre', db.String(15))
)
MOVIES = metadata_obj.tables['Movies']
query = db.select(MOVIES).filter(ilike_op(MOVIES.c.Movietitle, 'h%'))
result = engine.connect().execute(query).fetchall()
for record in result:
print("\n", record)
|
Output:
It fetches all the movie titles start with ‘h’ and ‘H’.
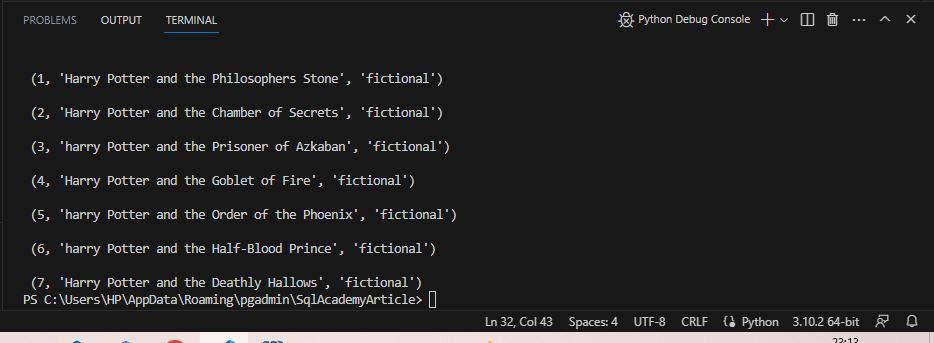
Output using ilike_op()
Demonstration
For complete explanation of code, you can go through this video tutorial.
Please Login to comment...