Architecture of an Embedded System | Set-3
Last Updated :
02 Dec, 2022
Typical embedded system mainly has two parts i.e., embedded hardware and embedded software. Embedded hardwares are based around microprocessors and microcontrollers, also include memory, bus, Input/Output, Controller, where as embedded software includes embedded operating systems, different applications and device drivers. Basically these two types of architecture i.e., Harvard architecture and Von Neumann architecture are used in embedded systems. Architecture of the Embedded System includes Sensor, Analog to Digital Converter, Memory, Processor, Digital to Analog Converter, and Actuators etc. The below figure illustrates the overview of basic architecture of embedded systems : 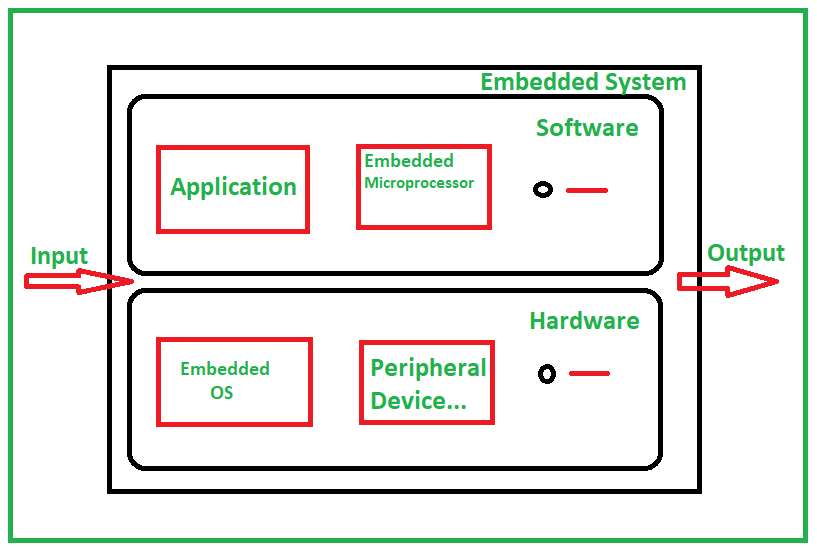
Embedded Product Development Life Cycle (EDLC) : Developing an embedded system or product mainly goes through this three phases which are –
1. Analysis
2. Design
3. Implementation
If we will go a little bit deeper to the development steps it includes these 7 steps :
- Requirement analysis
- Examine
- Design
- Develop
- Test
- Deploy
- Maintenance
Now Let’s discuss some of the advantages and disadvantages of Embedded systems. Advantages of Embedded System :
- Embedded systems are fast in performance.
- These systems consumes less power
- Small in shape and size.
- These systems are so scalable and reliable.
- Works on wide variety of sectors and environments.
- Improve product quality and enhance performance.
- Performs specific tasks without error.
Disadvantages of Embedded System :
- Difficult to backup of embedded files.
- Sometimes complex to develop.
- Integration may be a problem.
- Offer very limited resources for processing.
- Troubleshooting may be difficult.
- Maintenance may be a problem.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...