C Program for Program for array rotation
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
Write a function rotate(arr[], d, n) that rotates arr[] of size n by d elements.
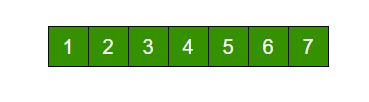
Rotation of the above array by 2 will make array

Method 1 (Rotate one by one):
leftRotate(arr[], d, n)
start
For i = 0 to i < d
Left rotate all elements of arr[] by one
end
To rotate by one, store arr[0] in a temporary variable temp, move arr[1] to arr[0], arr[2] to arr[1] …and finally temp to arr[n-1]
Let us take the same example arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], d = 2
Rotate arr[] by one 2 times
We get [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1] after first rotation and [ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2] after second rotation.
Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C
// C++ program to illustrate how to rotate array
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to rotate array left by one position
void leftRotateByOne(int arr[], int n)
{
int temp = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = temp;
}
// Function to rotate array left by d positions
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
leftRotateByOne(arr, n);
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
// Rotate array left by d positions
leftRotate(arr, d, n);
printf("Array after rotated by %d positions is: ", d);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
OutputArray after rotated by 2 positions is: 3 4 5 6 7 1 2
Method 2 (A Juggling Algorithm) :
This is an extension of method 2. Instead of moving one by one, divide the array in different sets
where number of sets is equal to GCD of n and d and move the elements within sets.
If GCD is 1 as is for the above example array (n = 7 and d =2), then elements will be moved within one set only, we just start with temp = arr[0] and keep moving arr[I+d] to arr[I] and finally store temp at the right place.
Here is an example for n =12 and d = 3. GCD is 3 and
Let arr[] be {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
a) Elements are first moved in first set – (See below
diagram for this movement)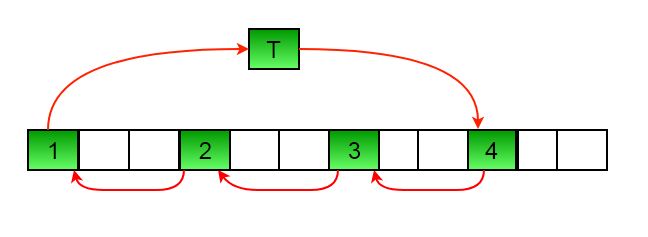
arr[] after this step --> {4 2 3 7 5 6 10 8 9 1 11 12}
b) Then in second set.
arr[] after this step --> {4 5 3 7 8 6 10 11 9 1 2 12}
c) Finally in third set.
arr[] after this step --> {4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3}Below is the implementation of the above approach :
C
// C program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <stdio.h>
/* function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size);
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b);
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
int i, j, k, temp;
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while (1) {
k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
leftRotate(arr, 2, 7);
printArray(arr, 7);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Output :
3 4 5 6 7 1 2
Time complexity : O(n)
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...