Difference Between Work and Energy
Last Updated :
24 Jun, 2022
Work: Work may be a sort of energy transfer. You are doing work on rock bottom whenever you walk and thus the bottom does work on you whenever you beat it. Moreover, it has to cover a distance during a selected direction with the help of the applied force for it to be considered work. It means the concept of labor hinges thereon on displacement. For work to occur there must be a force and movement from one place to another. The word “work” was first given by Gaspard Coriolis. He’s a French mathematician. He coined this word in 1826. The SI unit of physics is joules.
Formula of work
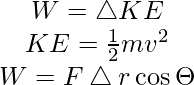
Energy: Energy can be defined as the measurement of the ability of something to do work. It is not a material substance. Energy can be stored and measured in many forms. It is also referred to as the force which works at a certain distance. Energy deals with the capacity of an object to do the work. The SI unit of physics is joules.
Formula of Energy
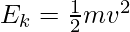
Here,
Ek = kinetic energy of object
m = mass of object
v = speed of object
Below is a table of differences between Work and Energy
S.No
| Work
| Energy
|
| 1 | Work is the ability to supply force and a change in distance to an object. | Energy is the ability to supply or create work. |
| 2 | There is a parallel relationship between the force components and displacement | Energy is the result of the work performed |
| 3 | The action did on the thing causing some displacement | It is described as a property of a system |
| 4 | Scalar units. | Scalar units. |
| 5 | Work = force × distance | There are various equations depending upon the kinds of energy |
| 6 | If the applied force is within the same direction of the displacement then work is positive | there is no direction component here because it is a scalar quantity |
| 7 | If the applied force is within the other way of the displacement that employment is negative | Then also there’ll be no direction component here because it may be a scalar quantity |
| 8 | Work was only utilized in 1826 | Energy was coined in 4 BC |
Sample Problems
Question 1: If a force of 30 N in lifting a load of 2kg to a height of 10m (g = 10ms-2), then calculate the amount of work done in this process?
Solution:
Given, Force in lifting mg = 30 N; height = 10 m
Work done W = ?
W = F.S (or) mgh
= 30 × 10
W = 300 J
Hence the answer is 300J
Question 2: Compute the work done if 10 N of force acts on the body showing the displacement of 2 m?
Solution:
Given, F (Force) = 10 N,
d (Displacement) = 2 m,
W (Work done) = F × d
= 10 N × 2 m
= 20 Nm.
Question 3: A body of mass 10kg at rest is subjected to a force of 16N. Find the K.E. at the top of 10 s.
Solution:
Mass m = 10 kg
Force F = 16 N
time t = 10 s
a = F/m
we know v = u + at
Kinetic energy KE: 1/2mv2
0.5 × 10 × 16 × 16
1280J
Question 4: A body of mass 5kg is thrown up vertically with a K.E. of 1000 J. If acceleration thanks to gravity is 10ms-2, find the peak at which the K.E. becomes half the first value.
Solution:
Mass m = 5kg
K.E Energy = 1000J
g = 10m s-2
At a height ‘h’, mgh = E/2
5 × 10 × h = 1000/2
h = 500/50
h = 10m
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...