Components of Ecosystem – Biotic and Abiotic
Last Updated :
05 Apr, 2024
The ecosystem is derived from the Greek word ‘Oikos’ which means home and ‘systema’ means system i.e a limited space in which living beings interact with each other and environmental factors. Every ecosystem consists of two components, namely, biotic components and abiotic components.
Biotic components refer to all living organisms in an ecology while abiotic components of an ecosystem are the non-living things. The components of an ecosystem are seen to function as a unit. In this article, we will cover the Ecosystem and its components notes.
What is Ecosystem?
The ecosystem is made of 2 factors i.e., biotic and abiotic components. Both components maintain an equilibrium in the ecosystem. The functional components of an ecosystem are:
- Abiotic factors
- Producers
- Consumers
- Decomposers
Components of Ecosystem
Ecosystem is mainly divided into 2 components i.e. Biotic and Abiotic Ecosystem. The flowchart of components of ecosystem is given below:
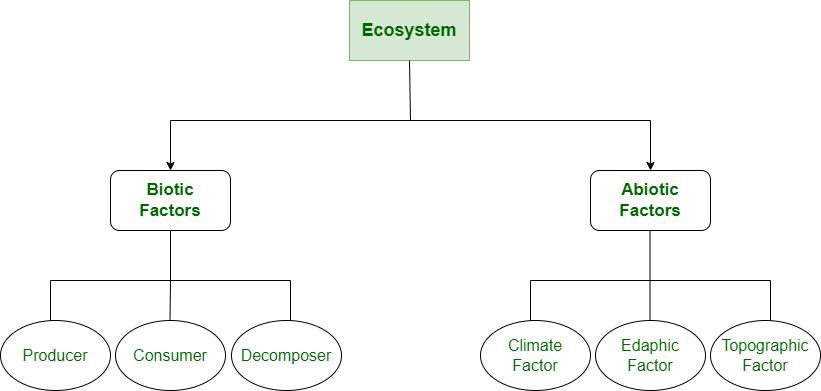
Abiotic Components of Ecosystem
Abiotic components of ecosystem is the non-living or physical components like air, weather, water, temperature, humidity, altitude, the pH level of soil, type of soil, etc. which affect living beings in terms of growth, development, maintenance, and reproduction. These are also known as ecological factors. These factors affect the life of species in all forms of environmental conditions such as in water or on land. Abiotic components change from one ecosystem to another. There are three types of abiotic components:
Edaphic Factors
Edaphic means floor or ground surface. This factor basically includes soil and substratum. The texture of the soil, its nutrient composition, and its density tell about the type of species or trees that will grow there.
Topographic Factors
This includes surface exposure altitude, slope, etc. Human activities lead to modification in these components. They have an impact on various biotic and abiotic factors. Such as farming, mining, and forest cutting.
Climate Factors
These factors are based on the atmosphere and include light, temperature, humidity, and wind. The speed of the wind and its direction influence the humidity of an area. Similarly, the temperature of the lives of many species for eg. Some species require a particular temperature to survive.
Effects of Abiotic Factors on Organism
An organism has many ways in which it responds to abiotic factors.
- Conformers: These organisms lack the ability to regulate their body temperatures, so they adapt themselves to the varying environmental conditions or migrate to other places.
- Regulators: These are those organisms that maintain their body conditions irrespective of the environment. For eg., humans maintain their body temperature at 37°C in both summer and winter.
- Migrate: There are many organisms that can not able to maintain their body conditions according to their respective environment. Such organisms in order to survive migrate to a region that suits their body conditions. For eg., the Siberian crane migrates to India when the conditions are not supportive of its survival.
- Diapause: It is a natural eruption in the development of some animals by the decrease of metabolic activity. Mostly found in insects, mites, a few crabs, and snails.
- Suspend: When the condition is not according to the organisms instead of migrating they enter a stage of suspension where their growth and development are suspended for a particular period of time. For eg., Bears went into hibernation in winter.
Biotic Components of Ecosystem
Biotic means are related to living. It contains all living components such as animal, plants, and the microorganisms like fungi, etc. As they use energy for their survival so on the basis of energy requirements they are divided into three parts:
Producer
Producers basically include trees that fulfill the requirements of other organisms for food and oxygen. Through photosynthesis, they gain the energy required by them under the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight.
Consumer
It includes carnivores, herbivores and omnivores. Carnivores depend on flesh for their food requirements. Herbivores eat plants and get energy from them. Omnivores eat both plants and flesh. Consumers help in maintaining the balance in the ecosystem by following the food chain.
Decomposer
These are also called saprophytes. These are the organisms that feed on dead and decay and convert them into organic compounds. They are important for the nutrient content in the soil. With more will be nutrients more species and trees can able to grow.
Also Read: Role of Decomposers in Ecosystem
Food Chain and Food Web
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. Whereas a food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem. A food chain usually starts with a producer and ends with a top carnivore.

The energy flow from one level to another level in a food chain gives the trophic level of an ecosystem. The producers come at first trophic level followed by herbivores (primary consumers), then small carnivores (secondary consumers) and large carnivores (tertiary consumers) occupy the fourth trophic level.
Conclusion – Ecosystem and its Components
Every ecosystem has two components, namely, biotic components and abiotic components. Biotic components refer to all living organisms in an ecology while abiotically refers to the non-living things. These biotic and abiotic interactions maintain the equilibrium in the environment. Various components of ecosystem are interdependent.
Also Read:
FAQs on Ecosystem and its Components
What is an Ecosystem?
Ecosystem is the area where both the biotic and abiotic components interact to live.
What are the Main Components of an Ecosystem?
The main components include biotic (living) elements like plants, animals, and microorganisms, and abiotic (nonliving) elements like sunlight, water, and soil.
What are the Different Types of an Ecosystem?
Ecosystems can be categorized into various types such as terrestrial (like forests and grasslands), aquatic (such as oceans, rivers, and lakes), and artificial (like urban areas and agricultural lands).
What are the Functions of an Ecosystem?
The main function of an ecosystem are: Productivity, nutrient cycling, regulating climate, and supporting biodiversity, all of which are essential for sustaining life on Earth.
What are the 5 Biotic Factors in an Ecosystem?
The 5 biotic factors in an ecosystem are: producers, consumers, herbivores, carnivores and omnivores. They are all the living components that interact with one another.
How do Ecosystems Function?
Ecosystems function through the interaction of their components, enabling the flow of energy and matter, supporting life processes, and maintaining ecological balance.
What is the Importance of Ecosystems?
Ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity, providing habitat, food sources, and essential services like air and water purification, climate regulation, and pollination.
How can Ecosystems be Classified?
Ecosystems can be classified into major types such as terrestrial (forest, grassland, desert) and aquatic (freshwater, marine, estuarine).
What Role do Humans Play in Ecosystems?
Humans impact ecosystems through activities like agriculture, urbanization, and pollution, but they also play a role in conservation and sustainable management efforts.
What is Ecosystem and its Components Class 10?
Ecosystem comprises living organisms (biotic factors) and non-living components (abiotic factors) like soil, water, air, sunlight, temperature, and nutrients. They interact to create a complex system exchanging energy and matter.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...