Finding Integrand using Weedle’s Rule
Last Updated :
22 Dec, 2022
Given a function 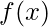 and two integers a and b. The task is to find the integrand of the given function from lower limit(a) to the upper limit(b) using Weedle’s Rule.
and two integers a and b. The task is to find the integrand of the given function from lower limit(a) to the upper limit(b) using Weedle’s Rule.
The given function is:
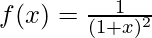
Examples:
Input: a = 0, b = 6
Output: 1.373448
Input: a = 10, b = 13
Output: f(x) = 0.022897
Approach:
The integration of any function 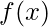 using Weedle’s Formula is given by:
using Weedle’s Formula is given by:
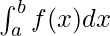 =
= 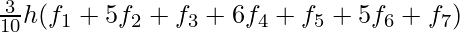
where,
h = 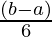
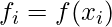 and i = [0, 6]
and i = [0, 6]
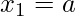
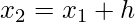
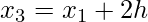
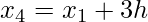
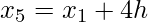
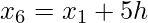
Below are the steps:
- Find the value of h from the above formula i.e., h =
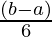 .
. - Find the value from
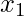 to
to 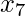 and calculate the value from
and calculate the value from 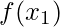 to
to 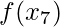
- Substitute the above values in Weedle’s Formula to find the integral value.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
float y(float x)
{
float num = 1;
float denom = 1.0 + x * x;
return num / denom;
}
float WeedleRule(float a, float b)
{
double h = (b - a) / 6;
float sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) * (y(a)
+ y(a + 2 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + h)
+ 6 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ y(a + 4 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + 5 * h)
+ y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum;
}
int main()
{
float a = 0, b = 6;
cout<< "f(x) = "<< fixed << WeedleRule(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
float y(float x)
{
float num = 1;
float denom = 1.0 + x * x;
return num / denom;
}
float WeedleRule(float a, float b)
{
double h = (b - a) / 6;
float sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) * (y(a)
+ y(a + 2 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + h)
+ 6 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ y(a + 4 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + 5 * h)
+ y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum;
}
int main()
{
float a = 0, b = 6;
printf("f(x) = %f", WeedleRule(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static float y(float x)
{
float num = 1;
float denom = (float)1.0 + x * x;
return num / denom;
}
static float WeedleRule(float a, float b)
{
float h = (b - a) / 6;
float sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) * (y(a)
+ y(a + 2 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + h)
+ 6 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ y(a + 4 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + 5 * h)
+ y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
float a = 0, b = 6;
float num=WeedleRule(a, b);
System.out.format("f(x) = "+"%.6f", num);
}
}
|
Python3
def y(x):
num = 1;
denom = float(1.0 + x * x);
return num / denom;
def WeedleRule(a, b):
h = (b - a) / 6;
sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) * (y(a)
+ y(a + 2 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + h)
+ 6 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ y(a + 4 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + 5 * h)
+ y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum;
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = 0;
b = 6;
num = WeedleRule(a, b);
print("f(x) = {0:.6f}".format(num));
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static float y(float x)
{
float num = 1;
float denom = (float)1.0 + x * x;
return num / denom;
}
static float WeedleRule(float a, float b)
{
float h = (b - a) / 6;
float sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) * (y(a)
+ y(a + 2 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + h)
+ 6 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ y(a + 4 * h)
+ 5 * y(a + 5 * h)
+ y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum;
}
public static void Main()
{
float a = 0, b = 6;
float num=WeedleRule(a, b);
Console.Write("f(x) = "+num);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function y(x)
{
let num = 1;
let denom = 1.0 + x * x;
return num / denom;
}
function WeedleRule(a, b)
{
let h = (b - a) / 6;
let sum = 0;
sum = sum + (((3 * h) / 10) *
(y(a) + y(a + 2 * h) + 5 * y(a + h) +
6 * y(a + 3 * h) + y(a + 4 * h) +
5 * y(a + 5 * h) + y(a + 6 * h)));
return sum.toFixed(6);
}
let a = 0, b = 6;
let num = WeedleRule(a, b);
document.write("f(x) = " + num);
</script>
|
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...