Global Mobile Satellite System
Last Updated :
06 Sep, 2021
GMSS stands for Global Mobile Satellite System. An artificial body which is placed in an orbit around the earth for the purpose of communication is known as Communication satellite. GMSS is a system which consists of various artificial communication satellites orbiting around the earth for the purpose of communication.
A satellite network is a combination of nodes that provides communication from one point on the Earth to another. A node in the network can be Satellite, an Earth station, or an End-user terminal or Telephone. Satellite networks are like cellular networks, they divide the planet into cells.
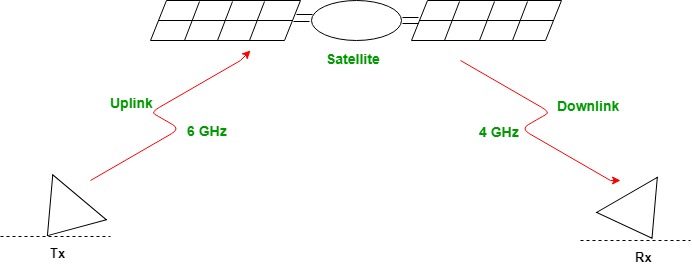
The frequencies reserved for the satellite microwave communication are in gigahertz(GHz) range. Each satellite sends and receives over two different bands. Transmission from earth to satellite is called the Uplink. Transmission from the satellite to the earth is called the Downlink.

Satellite frequency bands
Uplink and downlink frequencies must be different to avoid interference. Now, stations at the earth have greater power sources than that of satellite as it has only solar power. Also, higher frequency results in higher attenuation and to compensate with it more power is required. So, uplink uses higher frequency to penetrate the environment.
Satellite Orbits:
Orbit
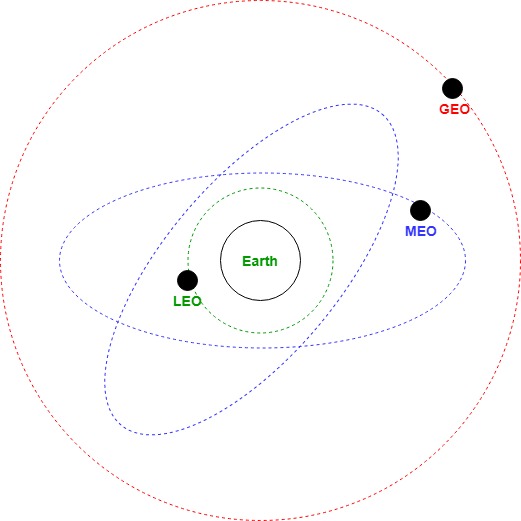
An artificial satellite needs to have an orbit, the path in which it travels around the Earth. The orbit can be equatorial, inclined or polar.
Footprint
Satellite process microwaves with bidirectional antennas. Therefore, the signal from the satellite is normally aimed at a specific area called the footprint.
Satellite Categories
Based on the location of the orbit, satellites can be divided into three categories as follows

GEO:
- GEO stands for Geostationary Earth Orbit.
- The communication satellites in this orbit operates at a distance of about 36000 km above the earth’s surface and their orbital time period is about 24 hours.
- Geostationary Orbit Satellites are used for radio broadcasting.
- To ensure constant communication, the satellite must move at the same speed as the earth, so that it seems to remain fixed above a certain spot. So such satellites are called geostationary.
- One geostationary satellite cannot cover the whole earth. One satellite in orbit has line-of-sight contact with vast number of stations, but the curvature of the Earth still keeps much of the planet out of sight. It takes minimum of three satellites equidistant from each other in geostationary Earth Orbit(GEO) to provide full global transmission.
MEO:
- MEO stands for Medium Earth Orbit.
- The communication satellites in this orbit operates at a distance of about 5000 to 12000 km above the earth’s surface.
- These satellites are positioned between the two Van Allen belts. A satellite at this orbit takes approximately 6 to 8 hours to circle the Earth.
- One Example of a MEO satellite system is Global Positioning System(GPS), constructed and operated by US Department of Defense, orbiting at an altitude about 18,000 km above the earth.
- The system consists of 24 satellites and is used for land, sea, and air navigation to provide time and locations for vehicle and ships.
- The orbits and the locations of the satellites in each orbit are designed in such a way that, at any time, four satellites are visible from any point on the Earth. A GPS receiver has a almanac that tells the current position of each satellite.
- GPS is based on a principle called Trilateration(also sometimes called Triangulation). Principle states that “On a plane, if we know our distance from three points, we know exactly where we are.”
LEO:
- LEO stands for Low Earth Orbit.
- The communication satellites in this orbit operates at a distance of about 500 to 1200 km above the earth’s surface and their orbital time period generally ranges between 95 to 120 minutes. The Satellite has a speed of 20,000 to 25,000 km/h. Low Orbit Satellites makes global radio coverage possible.
- An LEO system is made of a constellation of satellites that work together as a network, each satellite acts as a switch. Satellites that are close to each other are connected through inter-satellite links (ISLs). A mobile system communicates with the satellite through a user mobile link(UML). A satellite can also communicate with an Earth station(gateway) through a gateway link(GWL).
- LEO satellites can be divided into three categories: Little LEOs, Big LEOs, and Broad Band LEOs.
- Little LEOs operate under 1GHz. They are mostly used for low-data-rate messaging.
- Big LEOs operate between 1 and 3GHz. Globalstar and Iridium system are examples of Big LEOs.
- Broad Band LEOs provide communication similar to fiber-optic networks. The first broadband LEO system was Teledesic.
IRIDIUM:
- The concept of Iridium system, a 77-satellite network, was started by Motorola in 1990. The project took 8 years to materialize.
- Finally in 1998, the service was started by 66 satellites. The original name, Iridium, came from the name of the 77th chemical element. A more appropriate name is Dysprosium (the name of 66th element).
- The System has 66 satellites divided into 6 orbits, with 11 satellites in each orbit. The orbits are at an altitude of 750km.
- Iridium is designed to provide direct worldwide voice and data communication using handheld terminals, a service similar to cellular telephony but on a global scale.
Globalstar:
- Globalstar is LEO satellite system that uses 48 satellites in six polar orbits with each orbit hosting eight satellites. The orbits are located at an altitude of almost 1400km.
- The Globalstar system is similar to the Iridium system, the main difference is the relaying mechanism.
- Communication between two distinct users in Iridium system requires relaying between several satellites.
- Globalstar communication requires both satellites and earth station, which means that ground stations can create more powerful signals.
Teledesic:
- Teledesic is a system of satellites that provides fiber-optic like communication.
- Its main purpose is to provide broadband Internet access for users all over the world. It is sometimes called “Internet in the sky”.
- The project was started in1990 by Craig McCaw and Bill Gates, later other investors joined the consortium. Teledesic has 288 satellites in 12 LEO orbits, each at an altitude of 1350km.
- The commercial failure of the similar Iridium and Globalstar ventures and other systems, along with bankruptcy protection fillings, were the primary factors in halting this project, and Teledesic officially suspended its satellite construction work on 1 October 2002.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...