How to Permanently Disable Swap in Linux?
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2021
Swapping or swapping space is a physical memory page placed at the top of a disk partition or a special disk file that is used to expand a system’s RAM as the physical memory fills up. Inactive memory pages are often dumped into the swap area when no RAM is available, using this method of expanding RAM resources. However, swap space is much lower in transfer speeds and access time compared to RAM, due to the spinning speed of standard hard disks.
Reserving a small partition for swapping will significantly increase access time and speed transfer compared to conventional HDD on newer machines with fast SSD hard drives, but the speed is still lower than RAM memory. Some say that it is appropriate to set the swap space to twice the amount of computer RAM. However, swap space should be set to 2 or 4 GB on systems with more than 4 GB of RAM.
If your server has sufficient RAM memory or does not need the use of swap space or your device output is significantly reduced by swapping, you can consider disabling the swap field.
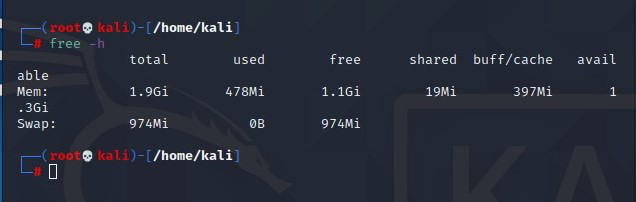
You first need to visualize your degree of memory load before actually disabling swap space, and then identify the partition that holds the swap area by issuing the commands below.
free -h
Look for the Used Swap Space size. If 0B or close to 0 bytes is the size used, it can be assumed that swap space is not used intensively and can be disabled for protection.
Next, check for TYPE=”swap” line after the blkid command to define the swap partition, as shown in the screenshot below.
blkid
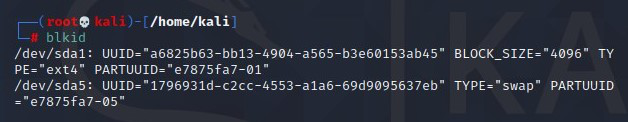
check swap partition type
Again, issue the following lsblk command to search and identify the [SWAP] partition as shown in the below screenshot.
lsblk
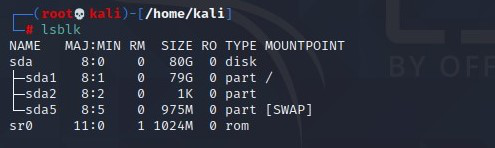
Search Confirm Swap Partition
Run the below command to deactivate the swap area after you have identified the swap partition or file.
swapoff /dev/mapper/centos-swap
Or disable all swaps from /proc/swaps.
swapoff -a
To check if the swap area has been disabled, run the free command.
free -h
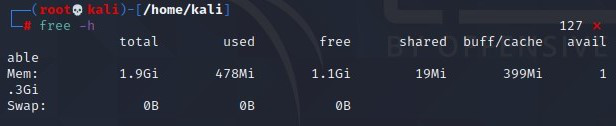
Disable Swap Partition
To permanently disable Linux swap space, open the /etc/fstab file, search for a swap line and add a # (hashtag) sign in front of the line to comment on the entire line, as shown in the screenshot below.
vi /etc/fstab
Afterwards, reboot the system in order to apply the new swap setting or issuing mount -a command in some cases might do the trick.
mount -a
After a system reboot, the commands presented at the beginning of this tutorial should be issued to indicate that the swap area in your system has been completely and permanently disabled.
free -h
blkid
lsblk
In simple ways or the other step:
If you really want to disable swapping (note: this is not suggested, even if you’re pretty sure there’s more than enough physical RAM), follow these steps:
- Run swapoff -a: this will immediately disable the swap.
- Remove any swap entry from /etc/fstab.
- Get the system rebooted. Ok, if the swap is gone. If it’s still here for some reason, you have to remove the swap partition.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 and, after that, use fdisk or parted to delete the (now unused) swap partition. Use great caution here: removing the wrong partition would have devastating results!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...