Mineral Requirements of Plants: Minerals are the naturally occurring inorganic nutrients found in food and soil that are necessary for the healthy functioning of the body. Minerals in food are essential for growth and survival. Micronutrients, such as boron and copper are needed by plants in tiny amounts, whereas macronutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are needed in larger quantities.
Plants require minerals for crucial roles in biochemical processes within the plant. In this article, we will cover the methods to study the mineral requirements of plants.
What are Minerals Elements?
Mineral elements, also known as mineral nutrients or simply minerals, are essential chemical elements that plants need for their growth and development. These elements are obtained by plants from the soil and are crucial for physiological processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and the formation of proteins, nucleic acids, and cell structures. A deficiency in any of these minerals lead to an abnormality in proper functioning of the body or diease. Around 105 mineral elements have been discovered so far.
What are Essential Mineral Elements in Plants?
Depending on the qualitative needs, mineral in plants have been divided into two broad categories:
Microminerals
Microminerals or micronutrients are essential minerals required by plants in relatively small quantities but are important for their growth and development. These elements include iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum, and chlorine, among others.
Macrominerals
Macrominerals are required by plants in relatively large quantities. These include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. Each macromineral has a crucial role in biochemical processes, such as photosynthesis, cell structure formation, and enzyme activation.
Methods to Study the Mineral Requirements of Plants
The methods to study the mineral requirements of plants are as follows:
Hydroponics
The method of growing plants without soil in nutrient-rich medium is called hydroponics, aquaculture, or soilless culture. The hydroponics was discovered by William Frederick Gericke in 1860. For example tomatoes, strawberries, and many other plants can grow through hydroponics techniques.
In a growing population, scientists believe hydroponic technology may be able to reduce impending food shortages. The hydroponic farming method is used to identify the signs of various nutrient deficiencies in plants and to identify crucial nutrients for the growth and development of the plant.
Hydroponic Nutrient Solution
Plants get 3 nutrients from the air – carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and 13 nutrients from supplemented water: nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, manganese, copper, zinc, boron, chlorine, and molybdate.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
The many types of Hydroponic systems are given below:
Ebb and Flow System
To provide stability, a medium like a perlite is needed. The tray containing the plants is periodically pumped with water and mineral solutions. The residual solution drains back into the reservoir after being absorbed by the plants. This straightforward approach is employed in backyard gardens. It is used to grow herbs.

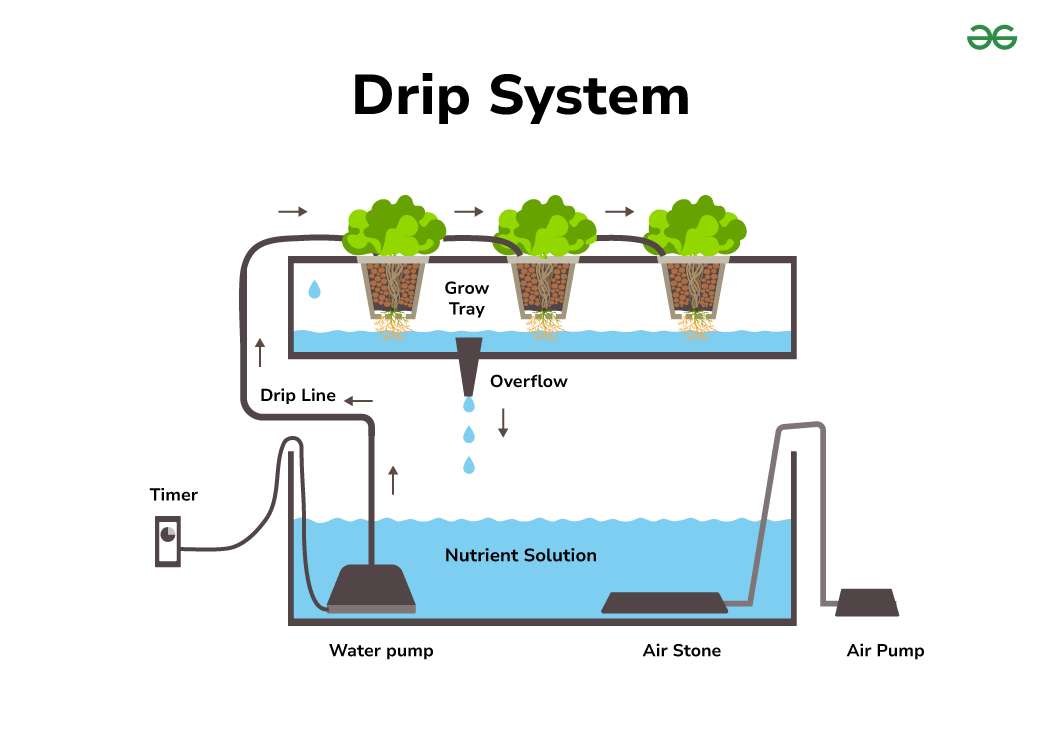
Drip Systems
Similar to ebb and flow, but with smaller tubes that drain onto the tops of the plants. Using this technique, little plants with less established root systems are cultivated.
Nutrient Film Technique
It is well-liked and adaptable. This system uses a pump to feed fertilized water to the grow tray and a drain pipe to recycle the used nutrient solution. The nutritional solution flows constantly over the roots in NFT due to gravity. A fresh solution is continuously poured into the high end of the tube, and the grow tray is angled to let the water flow down towards the drainpipe.
The thin film of nutritional solution that flows over the roots ensures that they are adequately nourished and moistened without drowning them. The thin film makes sure that the tops of the roots are dry and may access the air’s oxygen.

Nutrient Film Technique
Advantages of Nutrient Film Technique
- Efficient nutrient delivery directly to plant roots
- Continuous flow system ensures consistent moisture and oxygen access
- Reduced water usage compared to traditional soil-based methods
- Suitable for a wide range of plants and growing conditions
- Minimal space requirements, making it ideal for indoor or urban gardening.
Disadvantages of Nutrient Film Technique
- A whole crop can be destroyed by a failed pump in a matter of hours.
- Not recommended for use with plants that have extensive taproot systems.
- Fails miserably with plants that demand a lot of support.
Hydroponics Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of Hydroponics are discussed below:
Advantages of Hydroponics
- Plants grow more quickly, increasing the yield.
- Where traditional farming is not feasible, plants can be grown.
- Recycled and utilized nutrients and water.
- It is possible to grow organic food without using pesticides or fertilizers.
- A lot of space research programs use hydroponics.
- When there is no access to soil, food can be grown hydroponically away from the earth.
Disadvantages of Hydroponics
- Costly to set up. A hydroponics system is more expensive to buy and construct than a conventional garden.
- Power outage or pump failure can quickly impact plant health
- Requires regular monitoring and maintenance of nutrient levels and pH
- Limited availability of nutrients may require supplementation
- Susceptible to diseases and pests if not properly managed
- Risk of waterborne diseases.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a hydroponic growing technique where plants are grown without soil and their roots are suspended in the air. Nutrients are delivered to the plants through a fine mist or aerosol, allowing for efficient absorption and oxygenation, promoting rapid growth and maximizing yields. Aeroponics produces healthier plants, much faster crop development rates, and higher yields since the roots have better access to oxygen.
How Does Aeroponics Works?
A soilless medium is used to hold the roots of the fruits and vegetables cultivated hydroponically. When it comes to hydroponic growing mediums, there are several choices. This comprises Rockwool, perlite, vermiculite, and coco coir. Depending on the plants one wants to grow, each of the mediums has its own advantages and disadvantages.
In order to allow the roots of the plants to hang in the air, the plants are suspended in their pots. A special nutrient-rich mist is frequently sprayed on the now accessible roots to provide the plants with the nutrition they require. In order to allow the roots to spread out freely, the plants are initially wrapped in pieces of foam and inserted inside miniature pots with a netted foundation. While the opposite end of the roots continuously receives enriched mist, one end of the roots is exposed to light.

Aeroponics
Advantages of Aeroponics
The advantages of aeroponics are:
- Efficient nutrient absorption due to direct misting onto roots
- Faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil methods
- Conservation of water and nutrients, as the system recirculates resources
- Reduced risk of soil-borne diseases and pests
- Ideal for vertical farming and limited space environments
Disadvantages of Aeroponics
The disadvantages of aeroponics are:
- High initial setup costs for equipment and infrastructure
- Requires precise control of nutrient mist delivery, pH levels, and humidity
- Susceptible to system malfunctions or power outages, risking plant health
- Vulnerable to diseases and pathogens due to the exposed root system
- Greater expertise and knowledge needed for successful implementation compared to traditional gardening methods
Sand Culture
Sand culture is a hydroponic method where plants are grown in a medium consisting primarily of sand, which provides support while allowing roots access to nutrients and oxygen. Nutrient solutions are regularly applied to the sand to provide essential elements for plant growth, making it an efficient system for studying plant nutrition and root development.
Advantages of Sand Culture
The advantages of sand culture are given below:
- Provides excellent support for plant roots while allowing for proper aeration and drainage
- Easy to control nutrient levels and pH of the growing medium
- Ideal for studying plant nutrition and root development due to its simplicity and versatility
- Can be a cost-effective option for hydroponic growing, as sand is often readily available
- Minimal risk of diseases and pests compared to soil-based cultivation
Disadvantages of Sand Culture
The disadvantages of sand culture are given below:
- Sand must first be rinsed with add because it is naturally very alkaline;
- The sand becomes very warm in the summer and very cold in the winter, potentially harming plant roots;
- Limited water retention capacity, requiring frequent watering or nutrient solution application
- Susceptible to nutrient leaching, leading to inconsistent nutrient availability for plants
- Sand particles may compact over time, reducing aeration and root growth
- Greater risk of nutrient imbalances or deficiencies compared to other hydroponic methods
Difference between Hydroponics and Aeroponics
Hydroponics vs aeroponics is given below in tabular form:
|
Hydroponics
|
Aeroponics
|
| In hydroponics cultivating plants in nutrients rich water. |
Cultivating plants where roots are exposed to air. |
| Required lots of water. |
Required less water. |
| Include types of aquaponics and aeroponics. |
Include types of hydroponics. |
| Somewhat expensive. |
Have to establish indoors. |
| Used to hold the plant (clay, sand, or gravel). |
No such medium is used. |
Functions of Essential Mineral Elements
Plants need essential elements for plant growth and disease prevention and provide the energy required for the metabolic system.
- Phosphorus: By aiding in the transfer of carbohydrates, phosphorus promotes proper root growth and fruit ripening.
- Nitrogen: Enables the plant to capture sunlight energy by photosynthesis, driving plant growth and grain yield.
- Potassium: Plants require nitrogen to activate enzymes like DNA polymerase is potassium.
- Sulfur: It is necessary for the synthesis of proteins, amino acids, and oils.
- Magnesium: It is the primary, divalent atom of chlorophyll. Since they are necessary for photosynthesis
- Calcium: The proper functioning of the cell membrane as well as cell division. This mineral also regulates metabolic processes.
- Copper: Necessary for the respiration process. Activate a number of enzymes. Participates in the metabolism of cell walls.
- Manganese: It’s necessary for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is made with the help of manganese.
- Iron: It is needed in higher concentrations. It helps in the activation of enzymes and is a crucial component of protein.
- Boron: Boron is crucial for controlling plant hormone levels and fostering healthy growth.
- Chlorine: The evolution of oxygen in photosynthesis, and disease resistance and tolerance are only a few of its roles in plant growth and development.
Conclusion – Mineral Requirements Of Plants
In conclusion, understanding the mineral requirements of plants is vital for their growth and development. Minerals, whether micronutrients or macronutrients, play crucial roles in various biochemical processes within plants, influencing their overall health and productivity. Methods like hydroponics, aeroponics, and sand culture offer efficient ways to study and provide essential minerals to plants. By recognizing the significance of mineral elements and their functions, we can better nurture and sustain healthy plant growth, contributing to food security and agricultural advancements.
Also Read:
FAQs on Mineral Requirements of Plants
What Elements are Essential?
A plant cannot complete its life cycle without an essential element, which plays a specific structural or physiological role in its activities of plants.
What is Hydroponics?
Solution culture is a method for growing plants without soil from seed to maturity in a suitable nutritional solution. This method of plant development is referred to as hydroponics or soilless growing.
Which Hydroponic Method is the Best?
The most dependable and well-liked hydroponic technique is called the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT). The fundamentals are pretty simple to comprehend.
What is Aeroponics?
The sort of hydroponic system in which roots are hung in the air over the nutrient solution, which is whipped into a nutritious mist by a motor-driven rotor, is known as an aeroponic system, according to the answer.
What is the Sand Culture Technique?
Plants can be grown hydroponically using sand culture. To grow herbs, flowers, and veggies, utilize this technique. Instead of using soil to attach plants, this method creates a bed of gravel and sand. This technique is quite effective and is often utilized in arid and dry middle eastern countries.
Why are Minerals Important to Plants?
Minerals are important to plants because they are essential for various biochemical processes, such as photosynthesis and protein synthesis, which are vital for plant growth and development.
What is a Method to Study Minaral Requirements of Plants?
A method to study mineral requirements of plants is through hydroponics, where plants are grown in a nutrient-rich solution without soil, allowing precise control and observation of mineral uptake and plant response.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...