Mobile Forensics – Definition, Uses, and Principles
Last Updated :
04 Mar, 2022
Mobile forensics, a subtype of digital forensics, is concerned with retrieving data from an electronic source. The recovery of evidence from mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets is the focus of mobile forensics. Because individuals rely on mobile devices for so much of their data sending, receiving, and searching, it is reasonable to assume that these devices hold a significant quantity of evidence that investigators may utilize.
Mobile devices may store a wide range of information, including phone records and text messages, as well as online search history and location data. We frequently associate mobile forensics with law enforcement, but they are not the only ones who may depend on evidence obtained from a mobile device.
Uses of Mobile Forensics:
The military uses mobile devices to gather intelligence when planning military operations or terrorist attacks. A corporation may use mobile evidence if it fears its intellectual property is being stolen or an employee is committing fraud. Businesses have been known to track employees’ personal usage of business devices in order to uncover evidence of illegal activity. Law enforcement, on the other hand, may be able to take advantage of mobile forensics by using electronic discovery to gather evidence in cases ranging from identity theft to homicide.
Process of Mobile Device Forensics:
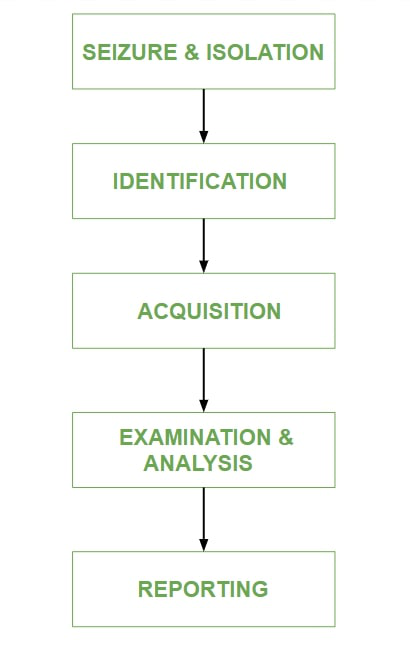
- Seizure and Isolation: According to digital forensics, evidence should always be adequately kept, analyzed, and accepted in a court of law. Mobile device seizures are followed by a slew of legal difficulties. The two main risks linked with this step of the mobile forensic method are lock activation and network / cellular connectivity.
- Identification: The identification purpose is to retrieve information from the mobile device. With the appropriate PIN, password, pattern, or biometrics, a locked screen may be opened. Passcodes are protected, but fingerprints are not. Apps, photos, SMSs, and messengers may all have comparable lock features. Encryption, on the other hand, provides security that is difficult to defeat on software and/or hardware level.
- Acquisition: Controlling data on mobile devices is difficult since the data itself is movable. Once messages or data are transmitted from a smartphone, control is gone. Despite the fact that various devices are capable of storing vast amounts of data, the data itself may be stored elsewhere. For example, data synchronization across devices and apps may be done either directly or via the cloud. Users of mobile devices commonly utilize services such as Apple’s iCloud and Microsoft’s One Drive, which exposes the possibility of data harvesting. As a result, investigators should be on the lookout for any signs that data may be able to transcend the mobile device from a physical object, as this might have an impact on the data collecting and even preservation process.
- Examination and analysis: Because data on mobile devices is transportable, it’s tough to keep track of it. When messages or data from a smartphone are moved, control is lost. Despite the fact that numerous devices can hold vast amounts of data, the data itself may be stored elsewhere.
- Reporting: The document or paper trail that shows the seizure, custody, control, transfer, analysis, and disposition of physical and electronic evidence is referred to as forensic reporting. It is the process of verifying how any type of evidence was collected, tracked, and safeguarded.
Principles of Mobile Forensics:
The purpose of mobile forensics is to extract digital evidence or relevant data from a mobile device while maintaining forensic integrity. To accomplish so, the mobile forensic technique must develop precise standards for securely seizing, isolating, transferring, preserving for investigation, and certifying digital evidence originating from mobile devices.
The process of mobile forensics is usually comparable to that of other fields of digital forensics. However, it is important to note that the mobile forensics process has its own unique characteristics that must be taken into account. The use of proper methods and guidelines is a must if the investigation of mobile devices is to give positive findings.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...