Python Tkinter – ListBox Widget
Last Updated :
29 Aug, 2022
Tkinter is a GUI toolkit used in python to make user-friendly GUIs.Tkinter is the most commonly used and the most basic GUI framework available in python. Tkinter uses an object-oriented approach to make GUIs.
Note: For more information, refer to Python GUI – tkinter
ListBox widget
The ListBox widget is used to display different types of items. These items must be of the same type of font and having the same font color. The items must also be of Text type. The user can select one or more items from the given list according to the requirement.
Syntax:
listbox = Listbox(root, bg, fg, bd, height, width, font, ..)
Optional parameters
- root – root window.
- bg – background colour
- fg – foreground colour
- bd – border
- height – height of the widget.
- width – width of the widget.
- font – Font type of the text.
- highlightcolor – The colour of the list items when focused.
- yscrollcommand – for scrolling vertically.
- xscrollcommand – for scrolling horizontally.
- cursor – The cursor on the widget which can be an arrow, a dot etc.
Common methods
- yview – allows the widget to be vertically scrollable.
- xview – allows the widget to be horizontally scrollable.
- get() – to get the list items in a given range.
- activate(index) – to select the lines with a specified index.
- size() – return the number of lines present.
- delete(start, last) – delete lines in the specified range.
- nearest(y) – returns the index of the nearest line.
- curseselection() – returns a tuple for all the line numbers that are being selected.
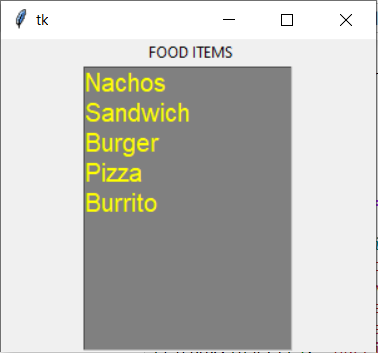
Example 1:
Python3
from tkinter import *
top = Tk()
listbox = Listbox(top, height = 10,
width = 15,
bg = "grey",
activestyle = 'dotbox',
font = "Helvetica",
fg = "yellow")
top.geometry("300x250")
label = Label(top, text = " FOOD ITEMS")
listbox.insert(1, "Nachos")
listbox.insert(2, "Sandwich")
listbox.insert(3, "Burger")
listbox.insert(4, "Pizza")
listbox.insert(5, "Burrito")
label.pack()
listbox.pack()
top.mainloop()
|
Output:
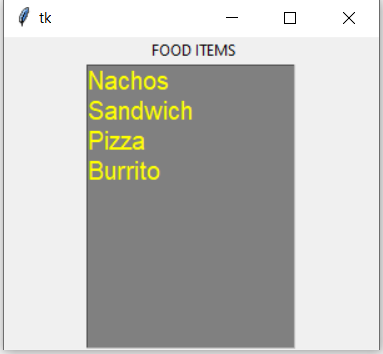
Example 2: Let’s Delete the elements from the above created listbox
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...