Socio-technical Systems
Last Updated :
28 Nov, 2022
Software and hardware are interdependent. Without the hardware, a software is an abstraction. When you put hardware and software together, you create a system. This system will be able to carry out multiple complex computations and return the result to its environment. This illustrates one of the fundamental characteristics of the system. Socio-technical system is basically a study of how any technology is used and produced. This help us to identify the ethical errors in technical and social aspects of the systems. Socio-technical system is a mixture of people and technology. It consists of many items. These items are difficult to distinguish from each other because they all have close inter-relationships. Some of the items are shown in figure: 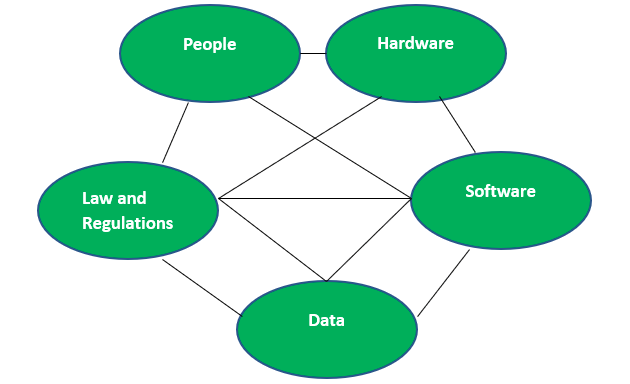 Socio-technical systems include:
Socio-technical systems include:
- People: People can be individuals or in groups. We also need to consider their roles and agencies. An organization employs the people, who build and make use of hardware and software, operate within law and regulations, and share and maintain the data.
- Hardware: The classical meaning if the technology is hardware. It involves mainframe, workstations, peripheral, connecting devices. There is no way for a socio-technical system to be without any kind of hardware component.
- Softwares: Software is nothing but an executable code. Softwares include operating system, utilities, application programs. Software is an integral part of the socio-technical system. Software often incorporates social rules and procedures as a part of the design, i.e. optimize these parameters, store the data in these format, ask for these data, etc.
- Law and regulations: There might be laws about the protection of privacy, or regulations of chips testing in military use, etc. Laws and regulations set by organization and government need to be followed. They carry special societal sanctions if the violators are caught.
- Data: The design of the socio-technical systems design involve what data are collected, to whom the data should be available and in which formats the data should be stored.
These Systems have properties that are perceptible when all the components are integrated and operate together. Example: Lets say, Software engineers in Silicon Valley may build a software with all sorts of bells and whistles expecting everyone to be tech savvy and without even considering the basic configuration of system requirements. If a large scale of people are in fact elderly and unaccustomed to the interface and have traditional systems operating on old technology then again the whole system will significantly reduced. That’s the reason we are interested not only in technical dimension but also domain of Socio-technical systems. The system include non-technical elements such as people, processes, regulations, goals, culture, etc., as well as technical components such as computers, software, infrastructure, etc. To understand socio-technical systems as a whole, you have to know the various layers, as shown in figure. 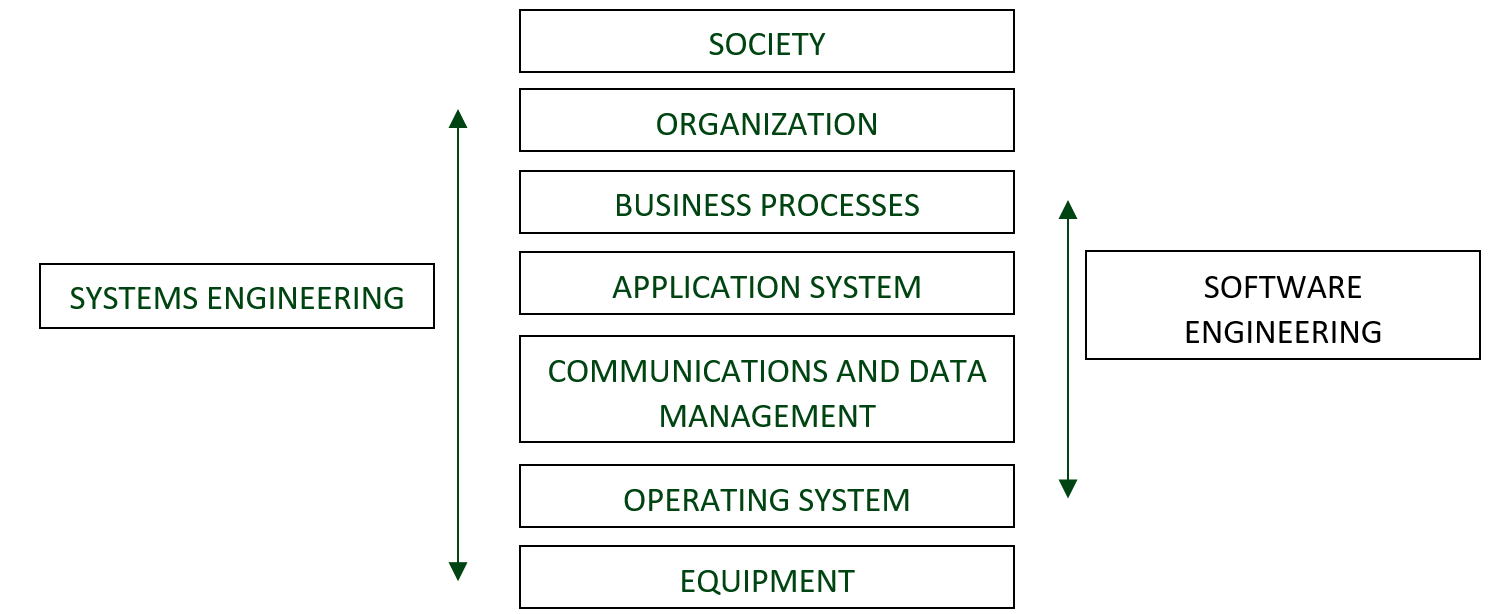 These systems can be impossible to understand. So, we refer to these 7 layers. These layers make up the Socio-technical systems stack.
These systems can be impossible to understand. So, we refer to these 7 layers. These layers make up the Socio-technical systems stack.
- The equipment layer: It contains set of hardware devices some of which may be computer, laptops, phones, etc. Most of the devices include embedded system of some kind.
- The operating system layer: This layer provides a set of common facilities for higher software layers in the system. This layer acts as an bridge to the hardware as it allows interaction between software and hardware.
- The communications and data management layer: This layer extends the operating system facilities and provides an interface that allows interaction with more extensive functionality, such as access to remote systems, access to a system database, etc. This is sometimes called middleware, as it is in between the application and the operating system.
- The application layer: This layer provides more specific functionality to meet some organization requirements. There may be many different application programs in this layer.
- The business process layer: This layer consists a set of processes involving people and computer systems that support the activities of the business. The use of software system, are defined and enacted.
- The organizational layer: At this level, the business rules, regulations, policies along with high-level strategic processes are defined and are to be followed when using the system.
- The social layer: Laws, regulations and culture that govern the operation of the system are defined.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...