SQL Query to Match Any Part of String
Last Updated :
19 Sep, 2023
It is used for searching a string or a sub-string to find a certain character or group of characters from a string. We can use the LIKE Operator of SQL to search sub-strings. The LIKE operator is used with the WHERE Clause to search a pattern in a string of columns. The LIKE operator is used in conjunction with the two wildcard characters.
- Percentage sign( % ): It represents zero, one, or multiple characters of variable length.
- Underscore ( _ ): It represents one, single character of fixed length.
The Syntax of a LIKE Clause is
SELECT Column1, Column2 FROM TableName WHERE Column LIKE [Expression];
Example:
In this example, we will create a schema for our database and name it Emp_details. After that, we will create a table inside it with the name Emp_data and try to search for a sub-string from the table’s data.
Step 1: Create a database
In order to create a database we need to use the CREATE operator.
CREATE DATABASE Emp_details;
USE Emp_details;
Step 2: Create a table inside the database
In this step, we will create the table Emp_data inside the Emp_details database.
CREATE TABLE Emp_data(id INT,
first_name VARCHAR(255),
last_name VARCHAR(255),
Salary VARCHAR(255),
Age INT,
PRIMARY KEY(id));
Step 3: Insert data into the table
In order to insert the data inside the database we need to use INSERT operator.
INSERT INTO Emp_data (id, first_name, last_name, Salary,Age)
VALUES (1, "Yash", "Kumar", 30000,25),
(2, "Rahul", "Yadav", 40000,22),
(3, "Mohit", "Kumar", 50000,21),
(4, "Ritik", "Kumar", 30000,23),
(5, "Shubham", "Pal", 20000,25);
Output:

Emp_data Table
Using LIKE Clause with % to match any number of Characters
Example 1: To fetch records from the Emp_data Table with first_name starting with the letter ‘Y%’.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE first_name LIKE 'Y%';
Output

output
Example 2: To fetch records from the Emp_data Table with first_name ending with the letter ‘%m’.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE first_name LIKE '%m';
Output

output
Example 3: To fetch records from the Emp_data with first_name with the letter ‘h’ at any position.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE first_name LIKE '%h%';
Output

output
Example4:
To fetch the records from Emp_data in which salary contains a number 50 in between.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE salary LIKE '%50%';
Output

output
Using LIKE Clause with _ to match only one Character
Example 1: To fetch records from the Emp_data Table with first_name ending any letter but starting from ‘R’.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE first_name LIKE 'R____';
Output

output
Example 2: To fetch a records from Emp_data table in which salary is starting with ‘3’ succeeding any two digits and finally ends with ’00’.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE Salary LIKE '3__00';
Output
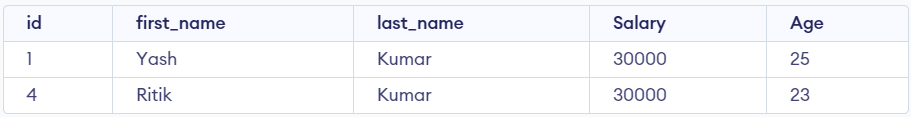
output
Example 3: To fetch records from the Emp_data Table with last_name starting with ‘K’.
Query
SELECT * FROM Emp_data WHERE last_name LIKE 'K____';
Output

output
Conclusion
To match any part of the string in SQL, we can use the LIKE operator with a wildcard. Typically, there are two types of wildcard operators utilized in SQL.
- %(percentage): It can represent either zero, one, or multiple characters with a variable length.
- _ (underscore): It is used to match only single character of a fixed length.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...