There are several forms are available to represent the equation of a straight line on the 2-dimensional coordinate plane, out of several forms three major forms are point-slope form, slope-intercept form, and general or standard form. General or standard form is a linear equation where the degree of the equation is one.
Standard form equation
The equation of standard form is
Ax + By + C = 0
Or
Ax + By = C
Here, A, B, and C are the real constant and the value of A and B is not zero simultaneously. So, we can say that an equation of Ax + By + C = 0 form where A and B is not zero simultaneously is known as the general equation of standard equation of a line. The graph of a standard equation is always straight.

If the value of A = 0 then the equation of the line is y = -C/B and the line is horizontal, means parallel to x-axis and if the value of B = 0, then the equation of the line is x = -C/A and the line is vertical, means parallel to y-axis.
For example:
2x + 4y + 3 = 0
4x – 6y = -34
Both the equations are in the standard form
3x = -3y – 2
3y = 2(x + 1)
Both the given equations are not in the standard form
Types of standard form
The standard form of the equation can of represented into three different forms:
Slope-Intercept form: As we know that the equation of slope-intercept form is y = mx + c. Now we see how to represent the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 in the Slope-intercept form.
So, if the value of B ≠ 0, then the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 can be written as:
 -(1)
-(1)
Now, compare the equation(1) with the slope intercept form,i.e. y = mx + c, we get
m = -A/B, and c = -C/B
Hence, the slope of the Ax + By + C = 0 is -A/B and the y-intercept is -C/B.
Examples:
Question 1. Find the slope and the y-intercept of the given equation, 2x + 5y + 1 = 0.
Solution:
Given: equation of line = 2x + 5y + 1 = 0
Find: slope and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
y = (-1 – 2x)/5
y = -2x/5 – 1/5 -(1)
As we know that the slope-intercept form is
y = mx + c -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
m = -2/5 and c = -1/5
Hence, the slope is -2/5 and y-intercept is -1/5
Question 2. Find the slope and the y-intercept of the given equation, 3x + 6y – 9 = 0.
Solution:
Given: equation of line = 3x + 6y – 9 = 0
Find: slope and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
y = (9 – 6x)/3
y = -2x + 3 -(1)
As we know that the slope-intercept form is
y = mx + c -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
m = -2 and c = 3
Hence, the slope is -2 and y-intercept is 3
Intercept Form: As we know that the intercept form of the equation is 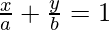 . Now we see how to represent the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 in the intercept form.
. Now we see how to represent the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 in the intercept form.
So, if the value of C ≠ 0, then the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 can be represented as:
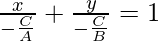 -(1)
-(1)
Now, compare the equation(1) with the intercept form,i.e. 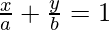 , we get
, we get
a = -C/A and b = -C/B
So, the x-intercept is -C/A and y-intercept is -C/B. And if the value of C = 0, then the general equation is Ax + By = 0, means the line is pass through origin so, it has zero intercept.
Examples:
Question 1. Find the x and y-intercept of the given equation, 4x + 8y + 2 = 0.
Solution:
Given: 4x + 8y + 2 = 0.
Find: x and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
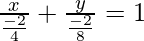 -(1)
-(1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
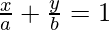 -(2)
-(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
a = -2/4 = -1/2
b = -2/8 = -1/4
So the x-intercept is -1/2 and y-intercept is -1/4
Question 2. Find the x and y-intercept of the given equation, 12x – 4y – 2 = 0.
Solution:
Given: 12x – 4y – 2 = 0
Find: x and y-intercept
So the given equation can be written as
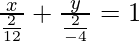 -(1)
-(1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
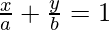 -(2)
-(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
a = 2/12 = 1/6
b = -2/4 = -1/2
So the x-intercept is 1/6 and y-intercept is -1/2
Normal Form: As we know that the intercept form of the equation is xcosω + ysinω = p. Now we see how to represent the general equation i.e., Ax + By + C = 0 in the normal form.
So let us considered the normal form is xcosω + ysinω = p of the line represented by the equation Ax + By + C = 0.
So, 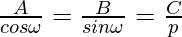
cosω = -Ap/C and sinω = -Bp/C
As we know that
sin2ω + cos2ω = 1 -(1)
So put all these value in equation (1), we get
(-Ap/C)2 + (-Bp/C)2 = 1
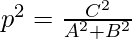

So, 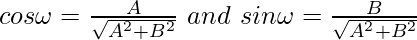
So, the normal form of the general equation is xcosω + ysinω = p.
Examples:
Question 1. Convert the given equation in the normal form 2x – 2y – 6 = 0.
Solution:
Given: 2x – 2y – 6 = 0
Divide the given equation
√(2)2 + (-2)2 = √4 + 4 = √8 = 2√2
So, 2x/2√2 – 2y/2√2 = 6/2√2
x/√2 – y/√2 = 3/√2 (1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
xcosω + ysinω = p -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
cosω = 1/√2
sinω = -1/√2
So, xcos45° + ysin225° = 3/√2
Question 2. Find the value of p and ω, equation is x + y + 3 = 0.
Solution:
Given: x + y + 3 = 0
Divide the given equation
√(1)2 + (1)2 = √2
So, x/√2 + y/√2 = -3/√2 (1)
As we know that the Intercept Form is
xcosω + ysinω = p -(2)
On comparing eq(1) and (2) we get
cosω = 1/√2
sinω = 1/√2
xcos45° + ysin45° = -3/√2
Hence, p = -3/√2 and ω = 45°
Graphing a linear equation: 5x + 2y = 20
To create a graph of the linear equation 5x + 2y = 20. We need to find the coordinates of the x-axis and y-axis.
Step 1: So, we solve for y:
5x + 2y = 20 -(1)
Subtract -5x on both side
5x – 5x + 2y = 20 – 5x
2y = 20 – 5x -(2)
Now divide equation (2) by 2, we get
2/2y = (20 – 5x)/2
y = 10 – 5x/2 -(3)
Now, we arrange equation(3) to the slope intercept form, i.e., y = mx + b
y = -5x/2 + 10
Now, the slope of the equation(m) is -5/2 and y-intercept(b) is 10.
Step 2: Now we create a table to find the points:
| x | y = 10 – 5x/2 | Points |
| 0 | y = 10-5(0)/2 | (0, 10) |
| 2 | y = 10 – 5(2)/2 | (2, 5) |
| 4 | y = 10 – 5(4)/2 | (4, 0) |
Step 3: After finding points, draw x-axis and y-axis on the graph and plot all these coordinates on the graph.
Step 4: Now draw a straight line by joining the points, here this straight line represents the given linear equation.

How to convert slope-intercept to standard form?
Let us discuss how to convert slope-intercept to standard form with the help of an example.
We have an equation y = 3/5x + 2/9. Now we convert the given equation into the standard form. Here, the given equation is written in slope-intercept form, i.e., y = mx + c, and we have to convert the given equation in standard form that is Ax + By + C = 0.
So, the given equation is multiplied by 45 on both sides, because 45 is divisible by 5 and 9
45y = 45(3x/5) + 45(2/9)
45y = 9(3x) + 5(2)
45y = 21x + 10
or 21x – 45y + 10 = 0
So, the standard form of the equation y = 3/5x + 2/9 is 21x – 45y + 10 = 0.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...