Sum of Hamming difference of consecutive numbers from 0 to N | Set 2
Last Updated :
12 May, 2021
Given a number N, the task is to find the sum of Hamming difference of consecutive numbers from 0 to N.
Hamming Distance between two integers is the number of bits which are different at the same position in both numbers.
Examples:
Input: 5
Output: 8
Explanation:
Difference between (0, 1) = 1, (1, 2) = 2,
(2, 3) = 1, (3, 4) = 3, (4, 5) = 1.
So the total sum is 1 + 2 + 1 + 3 + 1 = 8
Input: 9
Output: 16
Naive and Logarithmic Approach: Refer to Sum of bit differences for numbers from 0 to N for the naive approach and a logarithmic approach to calculate sum based on checking whether N as powers of 2 or not.
Approach: In this article, an approach based on observing the number of changes occurring in all the bits starting from the LSB to the MSB is discussed.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- It can be observed that the Least Significant Bit will change N times. The 2nd Least significant bit will change floor(N/2) times (i.e (N – 1)/2 if N is odd and N/2 if N is even). Hence, the ith bit will change floor(N/2i) times.
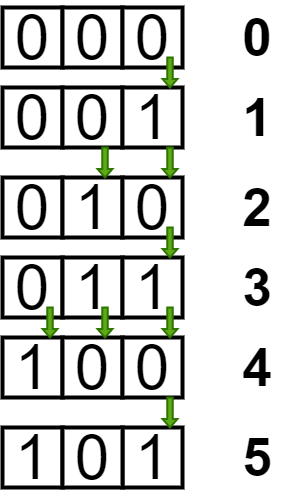
- Hence, to solve this problem we can simply store the sum
N + floor(N/2) + … floor(N/2i)
- until the term does not become zero.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int TotalHammingDistance(int n)
{
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while (n / i > 0) {
sum = sum + n / i;
i = i * 2;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int N = 9;
cout << TotalHammingDistance(N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int TotalHammingDistance(int n)
{
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while (n / i > 0)
{
sum = sum + n / i;
i = i * 2;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 9;
System.out.println(TotalHammingDistance(N));
}
}
|
Python3
def TotalHammingDistance(n):
i = 1
sum = 0
while (n // i > 0):
sum = sum + n // i
i = i * 2
return sum
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 9
print(TotalHammingDistance(N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int TotalHammingDistance(int n)
{
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while (n / i > 0)
{
sum = sum + n / i;
i = i * 2;
}
return sum;
}
public static void Main()
{
int N = 9;
Console.Write(TotalHammingDistance(N));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function TotalHammingDistance(n)
{
let i = 1, sum = 0;
while (Math.floor(n / i) > 0)
{
sum = sum + Math.floor(n / i);
i = i * 2;
}
return sum;
}
let N = 9;
document.write(TotalHammingDistance(N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(logN)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...