turtle.pos() method in Python
Last Updated :
01 Aug, 2020
The Turtle module provides turtle graphics primitives, in both object-oriented and procedure-oriented ways. Because it uses Tkinter for the underlying graphics, it needs a version of Python installed with Tk support.
turtle.pos()
This method is used to find the turtle’s current location (x, y), as a Vec2D-vector. This method has the Aliases: pos | position.
Syntax: turtle.pos() or turtle.position()
Return: turtle’s current location in terms of (x, y) coordinate
This function does not require any argument and returns the current position of the turtle in the format (x,y) where x and y represent the 2D vector. The default value is (0.0, 0.0).
Below is the implementation of the above method with some examples :
Example 1 :
Python3
import turtle
print(turtle.pos())
turtle.forward(150)
print(turtle.pos())
turtle.right(90)
turtle.forward(150)
print(turtle.pos())
|
Output:
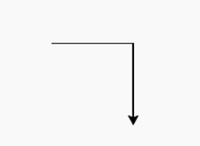
(0.0, 0.0)
(150.0, 0.0)
(150.0, -150.0)
Example 2:
Python3
import turtle
print(turtle.pos())
turtle.forward(40)
print(turtle.position())
turtle.right(45)
turtle.forward(40)
print(turtle.pos())
turtle.left(90)
turtle.forward(80)
print(turtle.pos())
turtle.right(90)
turtle.forward(40)
print(turtle.position())
turtle.left(45)
turtle.forward(40)
print(turtle.pos())
|
Output :
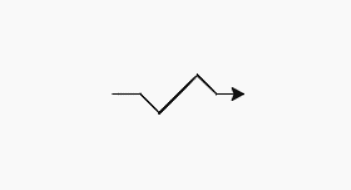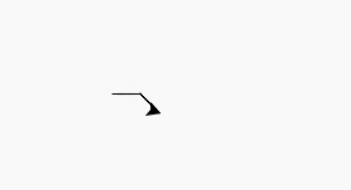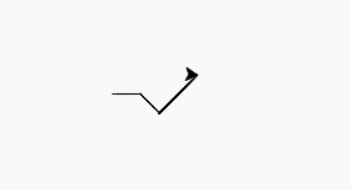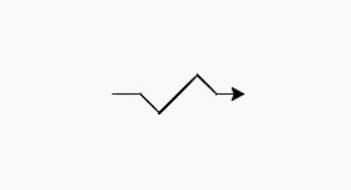
(0.0, 0.0)
(40.0, 0.0)
(68.2842712475, -28.2842712475)
(124.852813742, 28.2842712475)
(153.13708499, 0.0)
(193.13708499, 0.0)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...