Working of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Last Updated :
11 Aug, 2020
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used in networks to dynamically assign IP addresses & other network configuration information like default gateway, mask, DNS server address etc.
DHCP server automatically assigns IP address to various devices in network. This in turn reduces work of Network Administrator to manually assign IP address to various devices.
Automatic IP address assignment process undergoes four message exchange. These messages are abbreviated as Discover, Offer, Request & Acknowledgement (DORA). The following table gives the detail of these four messages.
| Message |
Detail |
| Discover |
This is message sent by DHCP client to discover a DHCP server. |
| Offer |
Sent by DHCP server to lease unique IP address and other parameters needed to client. |
| Request |
Sent by DHCP client asking server to lease parameters listed in Offer message. |
| Acknowledgement |
Sent by DHCP server to assign IP address, mask, default router & DNS server address to client. |
But there is conflict, DHCP IP address leasing uses layer 3 protocol i.e, Internet Protocol. This means that DHCP uses IP packets. But we know that hosts have no IP address initially then how they form IP packets? Actually they uses two reserved IP address for this purpose.
- 0.0.0.0 –
An IP address reserved to use as sender’s address for hosts that doesn’t have IP address assigned yet.
- 255.255.255.255 –
This is local broadcast IP address. Packets sent to this address are broadcast over local data link. Routers do not forward packet containing this address as destination address.
But, there’s still problem remaining. What if DHCP server is not available on local LAN and present outside of local LAN? DORA messages needs to be exchanged. For this purpose “IP helper address” which is actually IP address of DHCP server, is configured in routers.
Now packets containing 255.255.255.255 are updated to IP helper address as destination address. This helps DORA messages to exchanged outside of the local LAN.
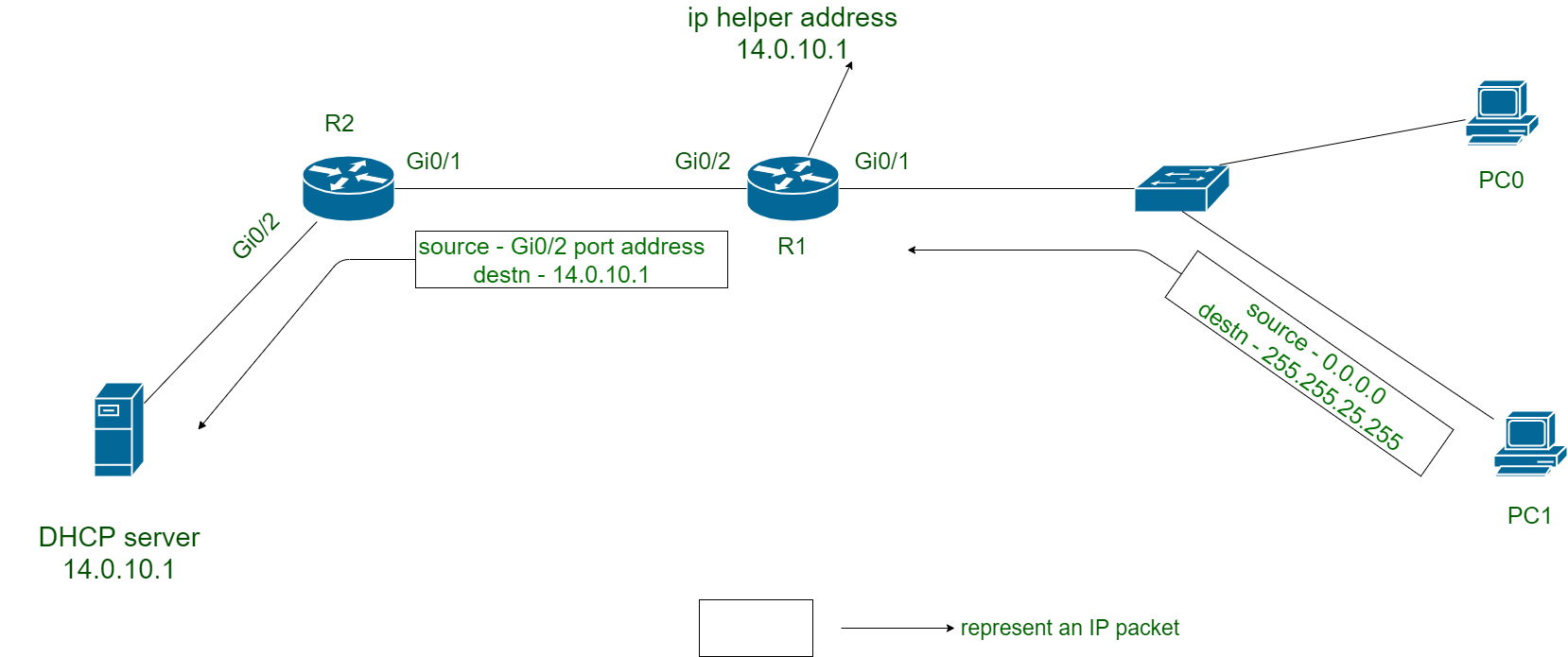
Figure – DHCP messages exchange with help of IP helper address
- PC1 sends Discover message but doesn’t find DHCP server in local LAN.
- R1 now receive IP packet and change destination address to DHCP server address i.e., 14.0.10.1 and sender address to its own outgoing interface address i.e., Gi0/2 interface address. R1 does this because of configuration of IP helper address.
- IP packet forwarded by R1 is received by DHCP server and respond to this Discover message.
- Server now send Offer message with source address as its own IP address and destination address as Gi0/2 interface address of R1. Actually it reverse the address of IP packet received.
- R1 receive the Offer message and forward it to PC1.
- Request and Acknowledge message are also exchanged as discussed in above steps.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...