Python program to solve quadratic equation
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2024
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree 2, which means it contains a term with a variable raised to the power of 2. It takes the form:
ax2 + bx + c = 0
where,
a, b, and c are coefficient and real numbers and also a ≠ 0.
If a is equal to 0 that equation is not valid quadratic equation.
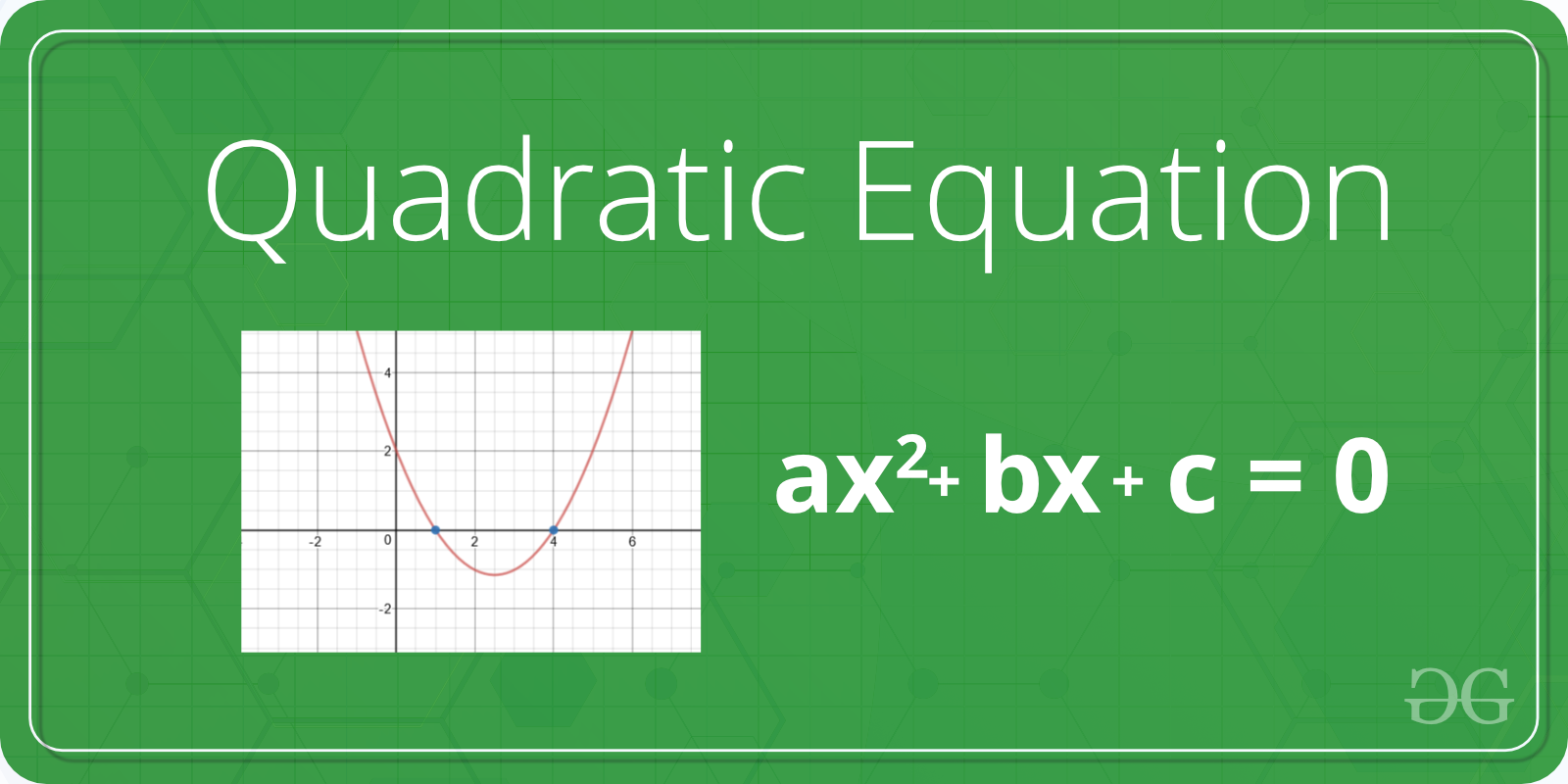 Examples:
Examples:
Input :a = 1, b = 2, c = 1
Output :
Roots are real and same
-1.0
Input :a = 2, b = 2, c = 1
Output :
Roots are complex
-0.5 + i 2.0
-0.5 - i 2.0
Input :a = 1, b = 10, c = -24
Output :
Roots are real and different
2.0
-12.0
Using the quadratic formula to Solve quadratic equations in Python
Using the direct formula Using the below quadratic formula we can find the root of the quadratic equation. 

The values of the roots depend on the term (b2 – 4ac) which is known as the discriminant (D). We have three cases of discriminant as given below:
Case 1: D > 0 (b*b > 4*a*c)
- Roots are real and different
- The roots are {-b + √(b2 – 4ac)}/2a and {-b – √(b2 – 4ac)}/2a
- For example, roots of x2 – 7x – 12 are 3 and 4
Case 2: D < 0 (b*b < 4*a*c)
- Roots are complex (not real)
- The discriminant can be written as (-1 * -D).
- As D is negative, -D will be positive.
- The roots are {-b ± √(-1*-D)} / 2a = {-b ± i√(-D)} / 2a = {-b ± i√-(b2 – 4ac)}/2a where i = √-1.
- For example roots of x2 + x + 1, roots are -0.5 + i1.73205 and -0.5 – i1.73205
Case 3: D = 0 (b*b == 4*a*c)
- Roots are real and equal
- The roots are (-b/2a)
- For example, roots of x2 – 2x + 1 are 1 and 1
Python3
# Python program to find roots of quadratic equation
import math
# function for finding roots
def equationroots( a, b, c):
# calculating discriminant using formula
dis = b * b - 4 * a * c
sqrt_val = math.sqrt(abs(dis))
# checking condition for discriminant
if dis > 0:
print("real and different roots")
print((-b + sqrt_val)/(2 * a))
print((-b - sqrt_val)/(2 * a))
elif dis == 0:
print("real and same roots")
print(-b / (2 * a))
# when discriminant is less than 0
else:
print("Complex Roots")
print(- b / (2 * a), + i, sqrt_val / (2 * a))
print(- b / (2 * a), - i, sqrt_val / (2 * a))
# Driver Program
a = 1
b = 10
c = -24
# If a is 0, then incorrect equation
if a == 0:
print("Input correct quadratic equation")
else:
equationroots(a, b, c)
Using the cmath module to solve quadratic equations in Python
First, we have to calculate the discriminant and then find two solutions to the quadratic equation using cmath module.
Python3
# import complex math module
import cmath
a = 1
b = 4
c = 2
# calculating the discriminant
dis = (b**2) - (4 * a*c)
# find two results
ans1 = (-b-cmath.sqrt(dis))/(2 * a)
ans2 = (-b + cmath.sqrt(dis))/(2 * a)
# printing the results
print('The roots are')
print(ans1)
print(ans2)
Output:
The roots are
(-3.414213562373095+0j)
(-0.5857864376269049+0j)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...