SQL UNION Operator
Last Updated :
22 Sep, 2023
The UNION operator could be used to find the result set or combination of two or more tables.
Terms and Conditions for using UNION
- Each table used within UNION must have the same number of columns.
- The columns must have the same data types.
- The columns in each table must be in the same order.
Syntax
SELECT columnnames FROM table1
UNION
SELECT columnnames FROM table2;
UNION operator provides only unique values by default. To find duplicate values, use UNION ALL.
Syntax
SELECT columnnames FROM table1
UNION ALL
SELECT columnnames FROM table2;
Let’s assume we have two tables “Emp1” and “Emp2”;
Query
Table1:
CREATE TABLE Emp1(
EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Country VARCHAR(50),
Age int(2),
mob int(10)
);
-- Insert some sample data into the Customers table
INSERT INTO Emp1 (EmpID, Name,Country, Age, mob)
VALUES (1, 'Shubham', 'India','23','738479734'),
(2, 'Aman ', 'Australia','21','436789555'),
(3, 'Naveen', 'Sri lanka','24','34873847'),
(4, 'Aditya', 'Austria','21','328440934'),
(5, 'Nishant', 'Spain','22','73248679');
Select * from Emp1;
Output
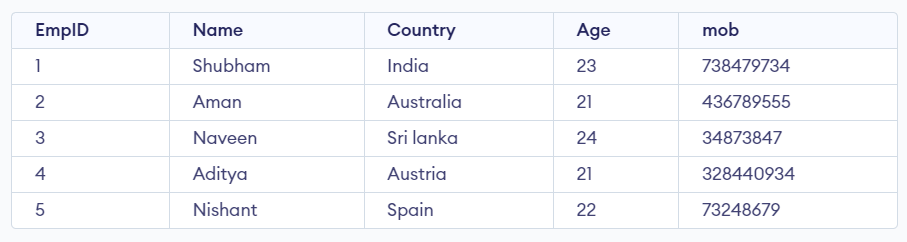
Emp1 Table
Query
Table2
CREATE TABLE Emp2(
EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Country VARCHAR(50),
Age int(2),
mob int(10)
);
-- Insert some sample data into the Customers table
INSERT INTO Emp2 (EmpID, Name,Country, Age, mob)
VALUES (1, 'Tommy', 'England','23','738985734'),
(2, 'Allen', 'France','21','43678055'),
(3, 'Nancy', 'India','24','34873847'),
(4, 'Adi', 'Ireland','21','320254934'),
(5, 'Sandy', 'Spain','22','70248679');
Select * from Emp2;
Output
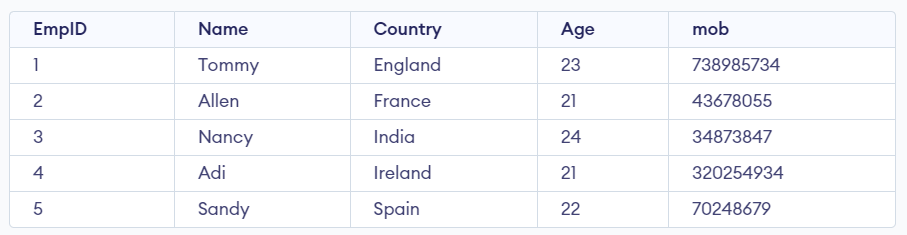
Emp2 Table
SQL UNION Example
The below SQL statement finds the cities (only unique values) from both the “Table1” and the “Table2” tables:
Query
SELECT Country
FROM Emp1
UNION
SELECT Country
FROM Emp2
ORDER BY Country;
Output

output
SQL UNION ALL Example
The below SQL statement finds the cities (duplicate values also) from both the “Emp1” and the “Emp2” tables:
Query
SELECT Country FROM Emp1 UNION SELECT Country FROM Emp2 ORDER BY Country;
Output
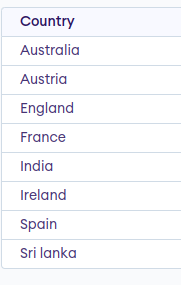
output
SQL UNION ALL With WHERE
The following SQL statement returns the cities (duplicate values also) from both the “Geeks1” and the “Geeks2” tables:
Query
SELECT Country, Name FROM Emp1
WHERE Name='Aditya'
UNION ALL
SELECT Country, Name FROM Emp2
WHERE Country='Ireland'
ORDER BY Country;
Output

output
Conclusion
We have studied about the SQL UNION command in this article. In order to summarize the article, the UNION command is used to aggregate the results of two or more SELECT statements from various tables and is useful when we need to gather records from two or more SELECT operations from two or more tables. The duplicate records from the SELECT are excluded from the UNION statement. Both SELECT queries must contain an identical number of columns in order to conduct the UNION operation; otherwise, the resulting expression will be incorrect.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...