Types of Cloud Computing
Last Updated :
06 May, 2024
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing in which a shared pool of resources is available over broad network access, these resources can be provisioned or released with minimum management efforts and service-provider interaction. In this article, we going to cover what is cloud computing, types of cloud Services, Deployment Models, and Types of Cloud Services.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a transforming way of business operations by offering scalable and flexible computing resources over the Internet. It facilitates organizations to access data, applications, and services from anywhere, at any time, resulting in increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Cloud computing makes free from the need for on-premises infrastructure and lets to empowers businesses to focus on innovation and growth rather than managing IT hardware.
To learn more about cloud computing refer to this – Article
What are the different types of Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing includes the cloud types such as Infrastructure as a Service ( IaaS ), Platform as a Service ( PaaS ), and Software as a Service ( SaaS ). In this IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, PaaS provides development and deployment platforms and SaaS provides software applications over the internet. These services are complemented by various deployment models such as public, private, hybrid and multicloud diverse business needs and preferences.
.webp)
Types Of Cloud Computing Models
In general, Cloud Computing Models are widely classified into 4 types. They are as follows:
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- It provides scalable and virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking over the internet.
- In this service, users can have full control over the infrastructure, having customization and management access of virtual machines, storage, and networking components.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- It provides a platform and a environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
- It offers tools and services such as development frameworks, databases, and middleware, streamlining the application development lifecycle.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- SaaS elivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, or update the software locally.
- With this service users can access the applications from any device with an internet connection, enabling flexibility and accessibility.
4. Serverless Computing
- Serverless computing provides abstracts for server management, facilitating developers to focus completely on developing and deploying code without managing servers.
- It automatically scales the resources based on demand, reducing the operational overhead and costs, and enabling rapid development and deployment of applications.
To know more about types of cloud services refer this – Article
Difference Between IaaS, PaaS, SaaS And Serverless
The following are the differences between IaaS, PaaS, SaaS and Serverless:
| Aspect |
IaaS |
PaaS |
SaaS |
Serverless Computing |
| Infrastructure |
It provides virtualized computing resources |
It provides the platform for application development |
It is used for fully developed software applications |
It provides an abstracted server management |
| Management |
Users manage virtual machines, storage, networking |
Platform provider manages underlying infrastructure |
Vendor fully manages and maintains the software |
Developers focus only on writing code |
| Customization |
High level of customization |
Limited customization options |
Minimal customization |
Focuses on code, less on infrastructure |
| Flexibility |
High |
Moderate |
Low |
High |
| Scalability |
Scalable at infrastructure level |
Scalable at application level |
Scalable at user level |
Automatically scales based on demand |
| Examples |
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure |
Google App Engine, Heroku |
Salesforce, Google Workspace |
AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions |
To know more about difference between types of cloud services refer this – Article
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
They are different approaches in managing and setting up the cloud services including cloud computing deployment models such as Public, private, hybrid, community and mulit-cloud deployments. These deployments provides scalability, control and flexibility with fulfilling special benefits meeting to various goals and demands of a business. In the below section we are discussing the types of cloud deployment models in more detail.
To know more about Cloud Computing Models – Article
What are the types of Cloud Services?
The following are the types of cloud also known as cloud deployment models as follows:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
- Multicloud
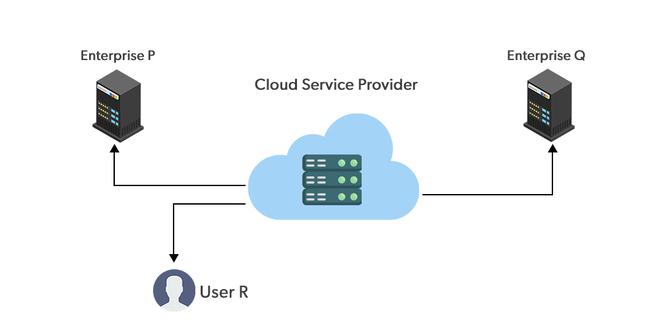
1. Public Cloud
- Public clouds are managed by third parties which provide cloud services over the internet to the public, these services are available as pay-as-you-go billing models.
- They offer solutions for minimizing IT infrastructure costs and become a good option for handling peak loads on the local infrastructure. Public clouds are the go-to option for small enterprises, which can start their businesses without large upfront investments by completely relying on public infrastructure for their IT needs.
- The fundamental characteristics of public clouds are multitenancy. A public cloud is meant to serve multiple users, not a single customer. A user requires a virtual computing environment that is separated, and most likely isolated, from other users.
Examples: Amazon EC2, IBM, Azure, GCP
Advantages of Public Cloud
The following are the advantages of public cloud:
- Public cloud is easily able to scale up and down resources as per the demand of traffic and workload. It facilitates with performance optimization and cost efficiency.
- It works on pay-as-you-go cloud model and helps in resolving the investments needs in hardware and infrastructure reducing overall costs.
Disadvantages of using Public Cloud
The following are the disadvantages of Public Cloud:
- It is difficult to trust and maintain data to a third-party provider may raise concerns about control and ownership
- The shared infrastructure of public cloud resources increases the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. It raises security and privacy concerns.
- Public cloud comes with limited transparency about the underlying infrastructure which may make it challenging to monitor and manage performance effectively.
2. Private cloud
- Private clouds are distributed systems that work on private infrastructure and provide the users with dynamic provisioning of computing resources. Instead of a pay-as-you-go model in private clouds, there could be other schemes that manage the usage of the cloud and proportionally billing of the different departments or sections of an enterprise. Private cloud providers are HP Data Centers, Ubuntu, Elastic-Private cloud, Microsoft, etc.
Examples: VMware vCloud Suite, OpenStack, Cisco Secure Cloud, Dell Cloud Solutions, HP Helion Eucalyptus

Advantages Of Private Cloud
- Customer information protection: In the private cloud security concerns are less since customer data and other sensitive information do not flow out of private infrastructure.
- Infrastructure ensuring SLAs: Private cloud provides specific operations such as appropriate clustering, data replication, system monitoring, and maintenance, disaster recovery, and other uptime services.
- Compliance with standard procedures and operations: Specific procedures have to be put in place when deploying and executing applications according to third-party compliance standards. This is not possible in the case of the public cloud.
Disadvantages Of Private Cloud
- The restricted area of operations: Private cloud is accessible within a particular area. So the area of accessibility is restricted.
- Expertise requires: In the private cloud security concerns are less since customer data and other sensitive information do not flow out of private infrastructure. Hence skilled people are required to manage & operate cloud services.
3. Hybrid cloud
- A hybrid cloud is a heterogeneous distributed system formed by combining facilities of the public cloud and private cloud. For this reason, they are also called heterogeneous clouds.
- A major drawback of private deployments is the inability to scale on-demand and efficiently address peak loads. Here public clouds are needed. Hence, a hybrid cloud takes advantage of both public and private clouds.
- Examples: AWS Outposts, Azure Stack, Google Anthos, IBM Cloud Satellite, Oracle Cloud at Customer

Advantages of using Hybrid cloud
The following are the advantages of using Hybrid Cloud:
- Hybrid cloud is available at a cheap cost than other clouds because it is formed by a distributed system.
- It works comes up with working fast with lower cost and facilitates in reducing the latency of the data transfer process.
- Most important thing is security. A hybrid cloud is totally safe and secure because it works on the distributed system network.
Disadvantages of Using Hybrid Cloud
The following are the disadvantages of using Hybrid Cloud:
- It’s possible that businesses lack the internal knowledge necessary to create such a hybrid environment. Managing security may also be more challenging. Different access levels and security considerations may apply in each environment.
- Managing a hybrid cloud may be more difficult. With all of the alternatives and choices available today, not to mention the new PaaS components and technologies that will be released every day going forward, public cloud and migration to public cloud are already complicated enough. It could just feel like a step too far to include hybrid.
- Community clouds are distributed systems created by integrating the services of different clouds to address the specific needs of an industry, a community, or a business sector. But sharing responsibilities among the organizations is difficult.
- In the community cloud, the infrastructure is shared between organizations that have shared concerns or tasks. An organization or a third party may manage the cloud.
- Examples: CloudSigma, Nextcloud, Synology C2, OwnCloud, Stratoscale

Advantages of Using Community Cloud
The following are the advantages of using Community Cloud:
- Because the entire cloud is shared by numerous enterprises or a community, community clouds are cost-effective.
- Because it works with every user, the community cloud is adaptable and scalable. Users can alter the documents according to their needs and requirements.
- Public cloud is less secure than the community cloud, which is more secure than private cloud.
- Thanks to community clouds, we may share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other capabilities between different enterprises.
Disadvantages of using Community Cloud
The following are the disadvantages of using Community Cloud:
- Not all businesses should choose community cloud.
- Gradual adoption of data
- It’s challenging for corporations to share duties.
Applications Of Community clouds
The following are the applications of community clouds:
- Media industry: Media companies are looking for quick, simple, low-cost ways for increasing the efficiency of content generation. Most media productions involve an extended ecosystem of partners. In particular, the creation of digital content is the outcome of a collaborative process that includes the movement of large data, massive compute-intensive rendering tasks, and complex workflow executions.
- Healthcare industry: In the healthcare industry community clouds are used to share information and knowledge on the global level with sensitive data in the private infrastructure.
- Energy and core industry: In these sectors, the community cloud is used to cluster a set of solution which collectively addresses the management, deployment, and orchestration of services and operations.
- Scientific research: In this organization with common interests in science share a large distributed infrastructure for scientific computing.
5. Multicloud
- Multicloud is the use of multiple cloud computing services from different providers, which allows organizations to use the best-suited services for their specific needs and avoid vendor lock-in.
- This allows organizations to take advantage of the different features and capabilities offered by different cloud providers.
- Examples: Cloud Foundry, Kubernetes, Apache Mesos, Red Hat OpenShift, Docker Swarm
Advantages of using Multi-Cloud
The following are the advantages of using multi-cloud:
- Flexibility: Using multiple cloud providers allows organizations to choose the best-suited services for their specific needs, and avoid vendor lock-in.
- Cost-effectiveness: Organizations can take advantage of the cost savings and pricing benefits offered by different cloud providers for different services.
- Improved performance: By distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, organizations can improve the performance and availability of their applications and services.
- Increased security: Organizations can increase the security of their data and applications by spreading them across multiple cloud providers and implementing different security strategies for each.
Disadvantages of using Multi-Cloud
The following are the disadvantages of using Multi-Cloud:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud providers and services can be complex and require specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Increased costs: The cost of managing multiple cloud providers and services can be higher than using a single provider.
- Compatibility issues: Different cloud providers may use different technologies and standards, which can cause compatibility issues and require additional resources to resolve.
- Limited interoperability: Different cloud providers may not be able to interoperate seamlessly, which can limit the ability to move data and applications between them.
Difference Between Public Cloud, Private Cloud And Hybrid Cloud
The following are the differences between public, private and Hybrid Clouds:
| Aspect |
Public Cloud |
Private Cloud |
Hybrid Cloud |
| Infrastructure |
It shares the resources among multiple organizations |
It is dedicated to a single organization |
It is combination of both public and private clouds |
| Cost |
It costs as per Pay-as-you-go model being cost-effective |
Its Initial investment for infrastructure, potentially higher operational costs |
It varies depending on usage of public and private resources |
| Control |
It have less control over infrastructure |
It has full control over infrastructure |
It varies, but typically more control than public cloud alone |
| Scalability |
It is highly scalable, resources available on-demand |
It is scalable, but may require additional investment for scaling |
It is scalable and facilitates with enhancing both public and private resources |
| Security |
Security is managed by cloud provider, varying levels of security measures |
Higher level of control over security measures |
Security concerns must be addressed for both public and private components |
| Flexibility |
Offers flexibility in resource allocation and usage |
Flexible, but may require additional setup and management |
Provides flexibility to leverage best of both public and private clouds |
| Examples |
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure |
Private clouds hosted on-premises or by third-party providers |
Organizations using a combination of public and private clouds, such as AWS Outposts or Azure Stack |
To know more about the difference between Public vs Private vs Hybrid Clouds – Article
Types Of Cloud Computing – FAQs
What are the 4 types of Cloud Computing?
Public, private, hybrid and multi clouds are the types of cloud computing.
What Are the 5 Types of Cloud Storage?
The five types of cloud storages are object storage, files storage, bock storage, archival storage and cold storage.
Who is the father of Cloud Computing?
Dr. Larry Roberts is widely considered as the father of cloud computing, who pioneered the concept of ARPANET.
Which Cloud Should I Use?
The Choosing of Cloud depends on serveral factors such as budget, scalability, security needs and its geographical locations. One should choose the cloud based on their requirement needs and which cloud is providing them effectively.
.Which Cloud Services Are more Costs?
Cloud service costs vary based on usage and services; comparing pricing structures and features is essential for accurate assessment.
Is Google Drive A Cloud Storage?
Yes, Google Drive is a cloud storage provided by Google. It facilitates users to access and store files and data from any device with the internet connection.
Which Cloud has the Best Resources?
Each Cloud platform offers many wide range of resources on compute, storage, networking and specialized services. The best choice of cloud depends on the specific requirements you are looking for.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...